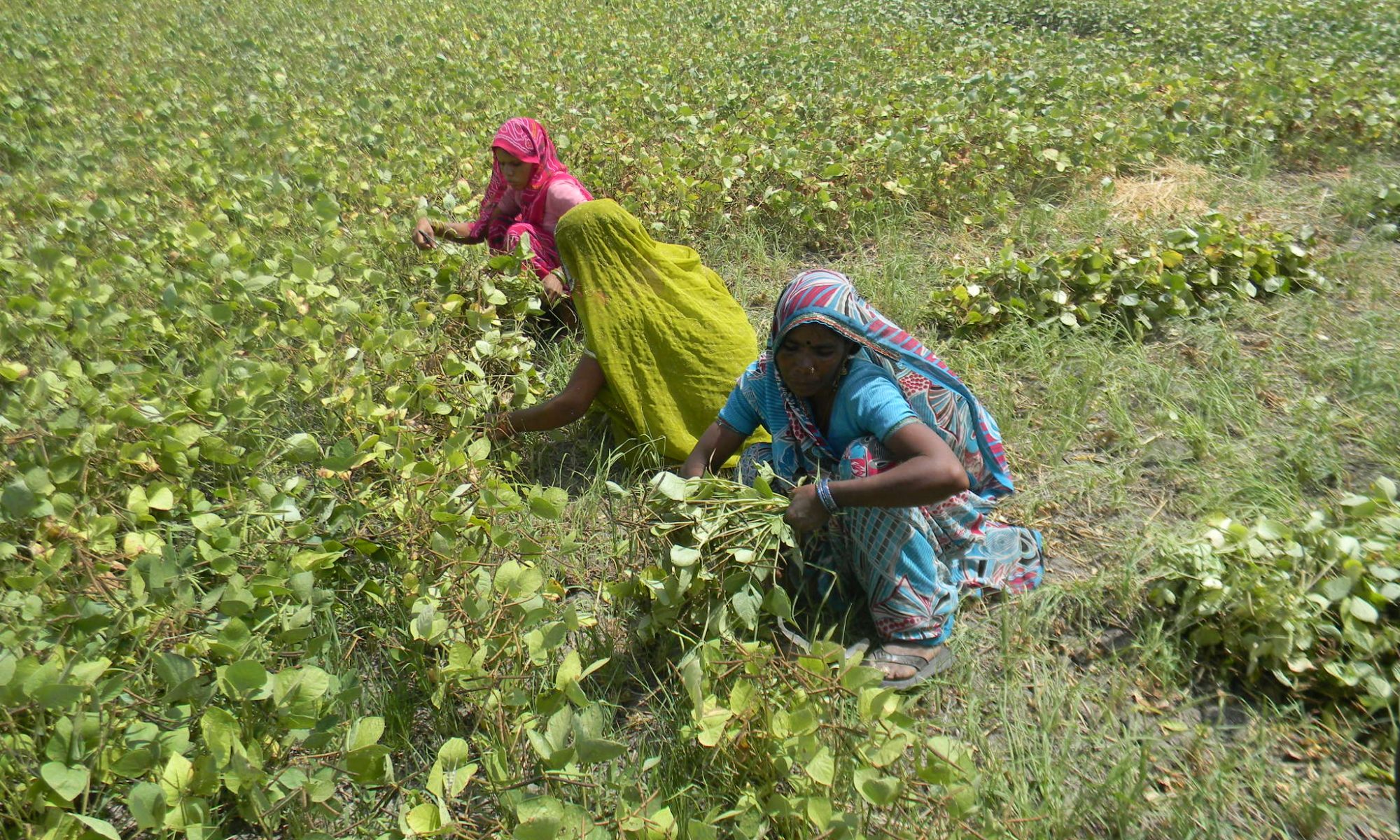
- The crop should be harvested when 80-85% of pods have matured.
- Paraquat @ 800 ml/acre can be sprayed using 150-200 litres of water for drying of crop foliage for combine harvesting of the crop.
- Harvesting process complete with the help of the sickle.
- During moong harvesting process do not uproot the plants.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on the button below.
Share