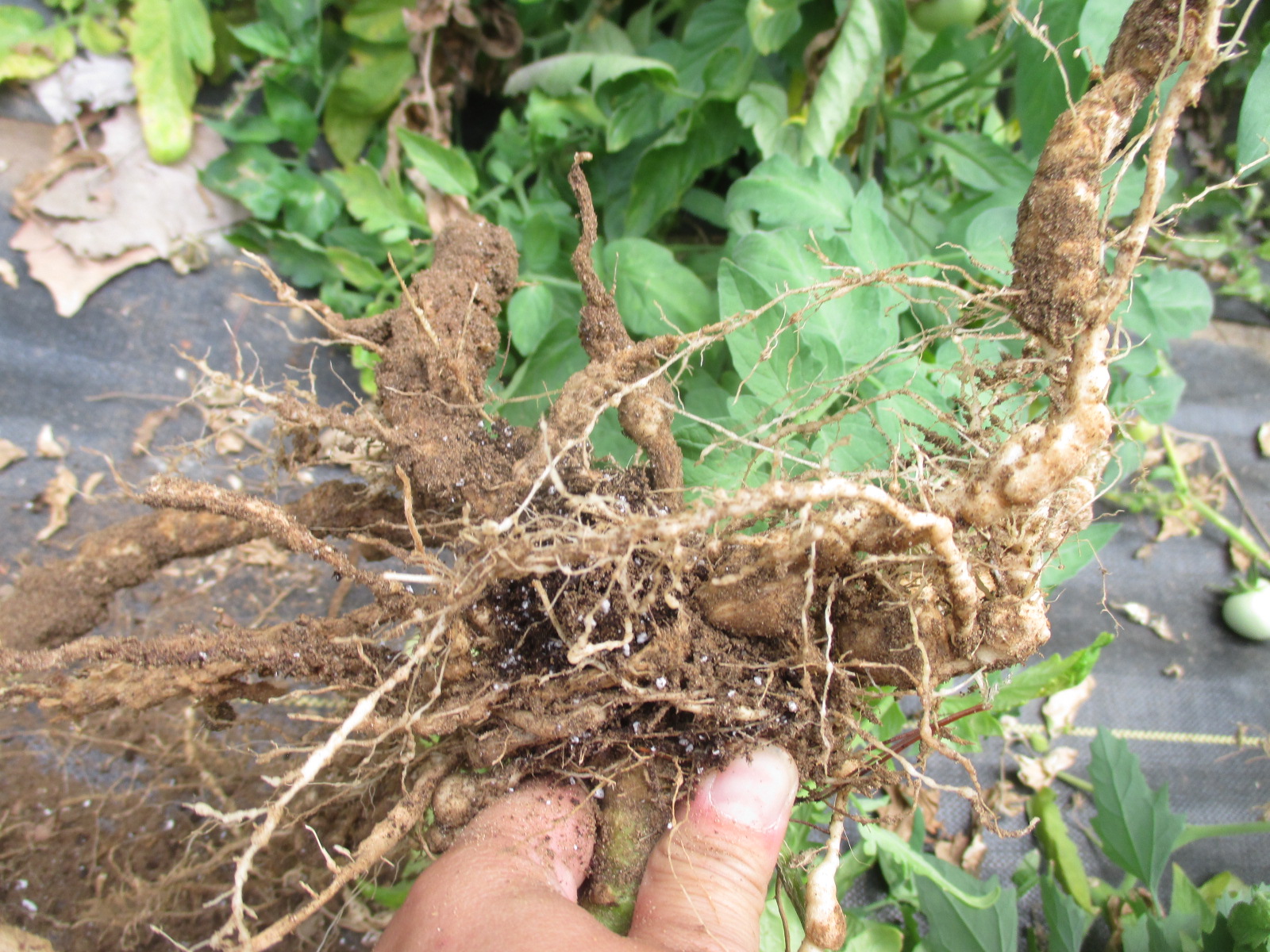
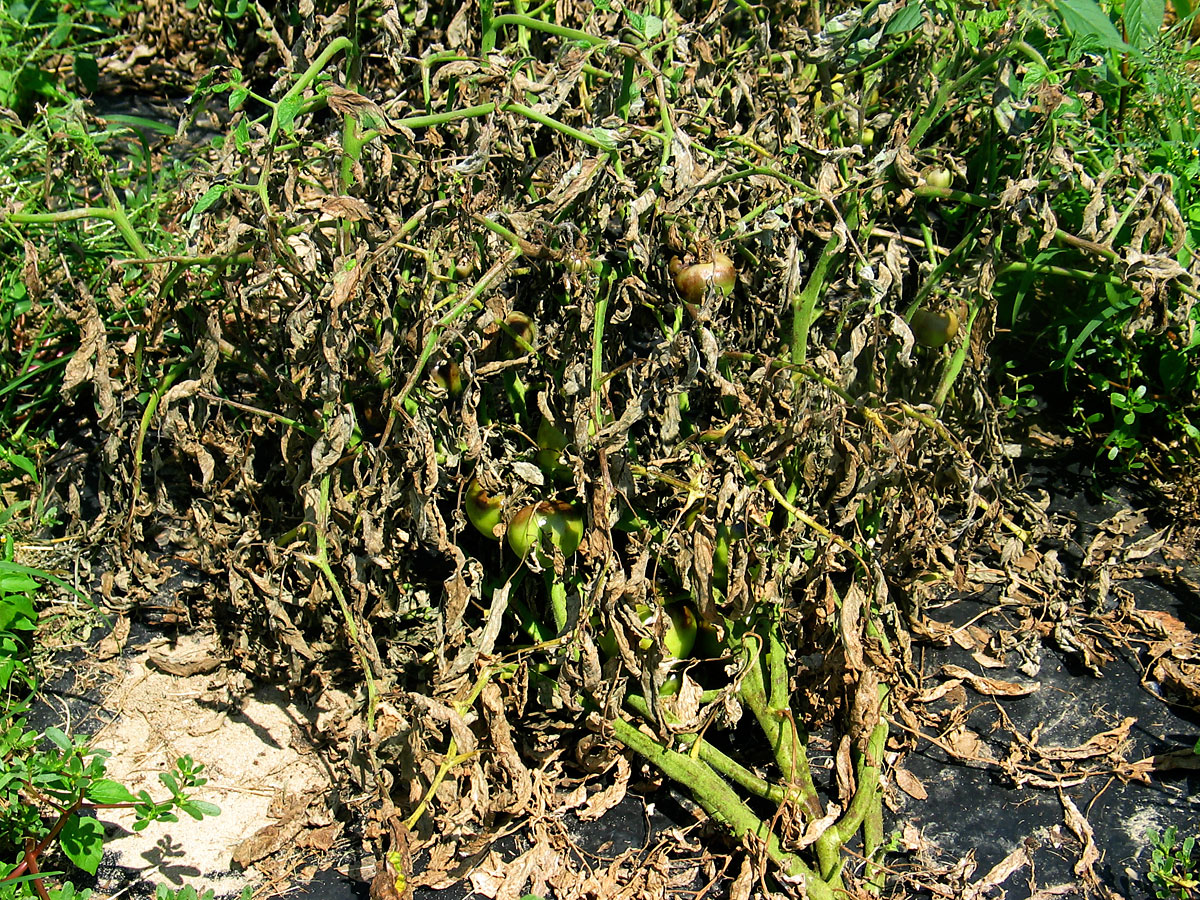
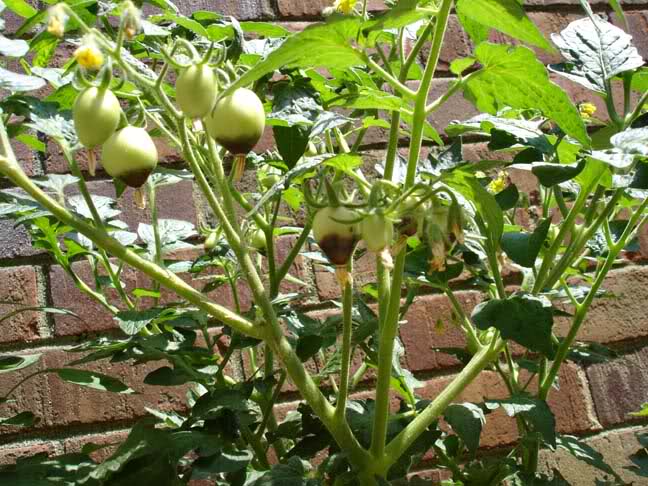
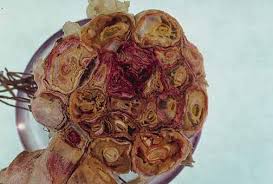
- Use resistant varieties.
- Do use deep summer plowing to control root-knot nematode.
- Neem cake at the rate of 80 Kg/Acre should be applied for effective control.
- Carbofuran 3G at the rate of 8 kg/acre should be applied as a soil treatment.
- Paecilomyces lilacinus-1% WP @ 10 g / kg seed for seed treatment, 50 gm / meter sq Nursery Treatment, 2 to 3 kg/ acre Soil application.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on the button below
Share