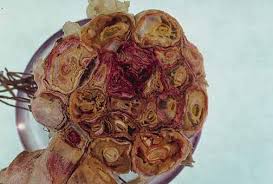
- Initially yellowing of leaves and stunted growth of the plant is observed, which later on dry from tip to downwards.
- In the early stage of infection, the roots of the plants become pink in colour and rotting take place later. In the advanced stage, the bulb starts decaying from lower ends and ultimately the whole plant dies.
- Survival and spread:- Pathogen survives in soil and garlic bulb as a primary source of inoculum in the form of Chlamydospore, resting spore) for many years.
- Favourable conditions:- Moist soil and 27 °C temperature favours the development of disease.
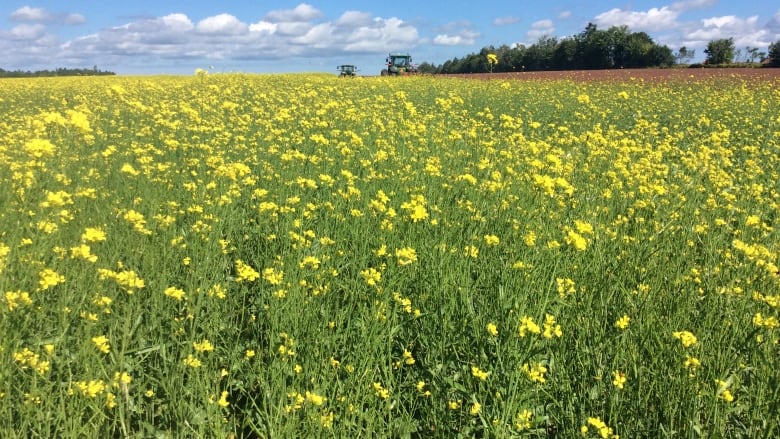
Manures and fertilisers for Mustard
Apply 6-8 tonnes of FYM or compost at the time of field preparation. And 25-40 kg nitrogen, 25 kg P2O5 and 16 kg K2O per acre.
ShareTime of sowing for mustard
- Toria or mustard should be sown from the mid to the last week of September. Sowing of sarson and rai must be completed in the last week of October.
- Spacing
- Generally, toria is planted in rows 30 cm apart while sarson and rai are sown in rows 45 cm apart. Thinning is done three weeks after sowing to maintain a plant to plant distance of 10 to 15 cm.
How to Control Cauliflower Diamondback moth
- For the prevention of diamondback moth, bold mustard should be sown in 2 lines after every 25 lines of cabbage/Cauliflower.
- Spray the crop with Profenofos 50% EC 500 ml/acre or Profenofos 40% EC + cypermethrin 4% EC @ 400 ml/acre or
- Spinosad 25% SC100 ml/acre or Indoxacarb @ 300 ml/acre or Emamectin Benzoate 5% SG @ 100 gm/acre Spray at fortnight intervals starting from 25 days after transplanting to control the pest.
- For biological control Beauveria bassiana @ 1kg/acre.
- Note: Mix the sticker with each spray.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on the button below.
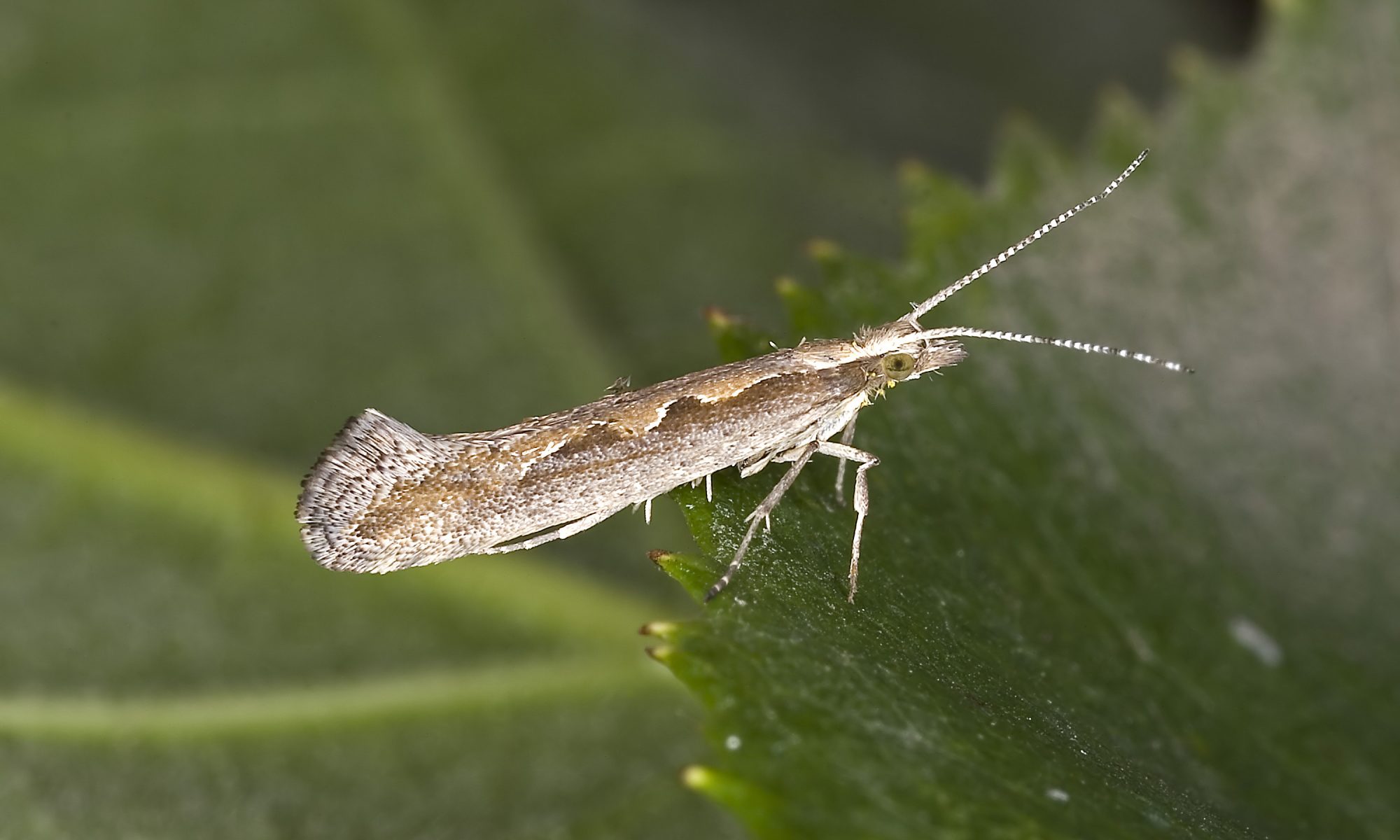
ShareCauliflower Diamondback moth
Identification
- Eggs are yellowish-white with greenish tings.
- The caterpillars are 7-12 mm in length, pale yellowish-green in colour with fine erect back hair scattered all over the body.
- Adults are 8-10 mm long greyish-brown in colour having pale whitish narrow wing inner yellow margins.
- The adult female lays eggs on the leaves either singly or in groups.
- White markings along the back of the fore wings which when folded from a diamond-shaped pattern in adult diamondback moth.
Damage
- Small slender green caterpillars on emergence feed on the leafs epidemics and later make holes in the leaves.
- Severely affected leaves are completely skeletonized.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on the button below.
ShareWhy, when and how to add mycorrhiza in the field :-
- Improve plant root growth and development
- Increase the uptake and mobilization of phosphate in all crops
- Increase and facilitate nutrient and translocation from the soil and root cuticle parenchyma to xylem ,Phloem, elements like nitrogen, potassium, Iron, manganese, magnesium, copper, zinc, boron, sulphur and molybdenum.
- Effective in overcoming the stress conditions like drought, disease incidence and deficiency of nutrients.
- Enhance product quality and increase immune power of the crop
- Its supplement root hair in water absorption hence prevents reduction in crop relative water content of cells and helps to overcome drought.
- Soil Treatment – Mix Premium mycorrhiza 4 kg per acre in 50 Kg of well decomposed Fym/compost/vermi compost/field soil and incorporated in the soil before sowing/transplant.
- Broadcast the above mixture in standing crop 25-30 days after sowing.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on the button below
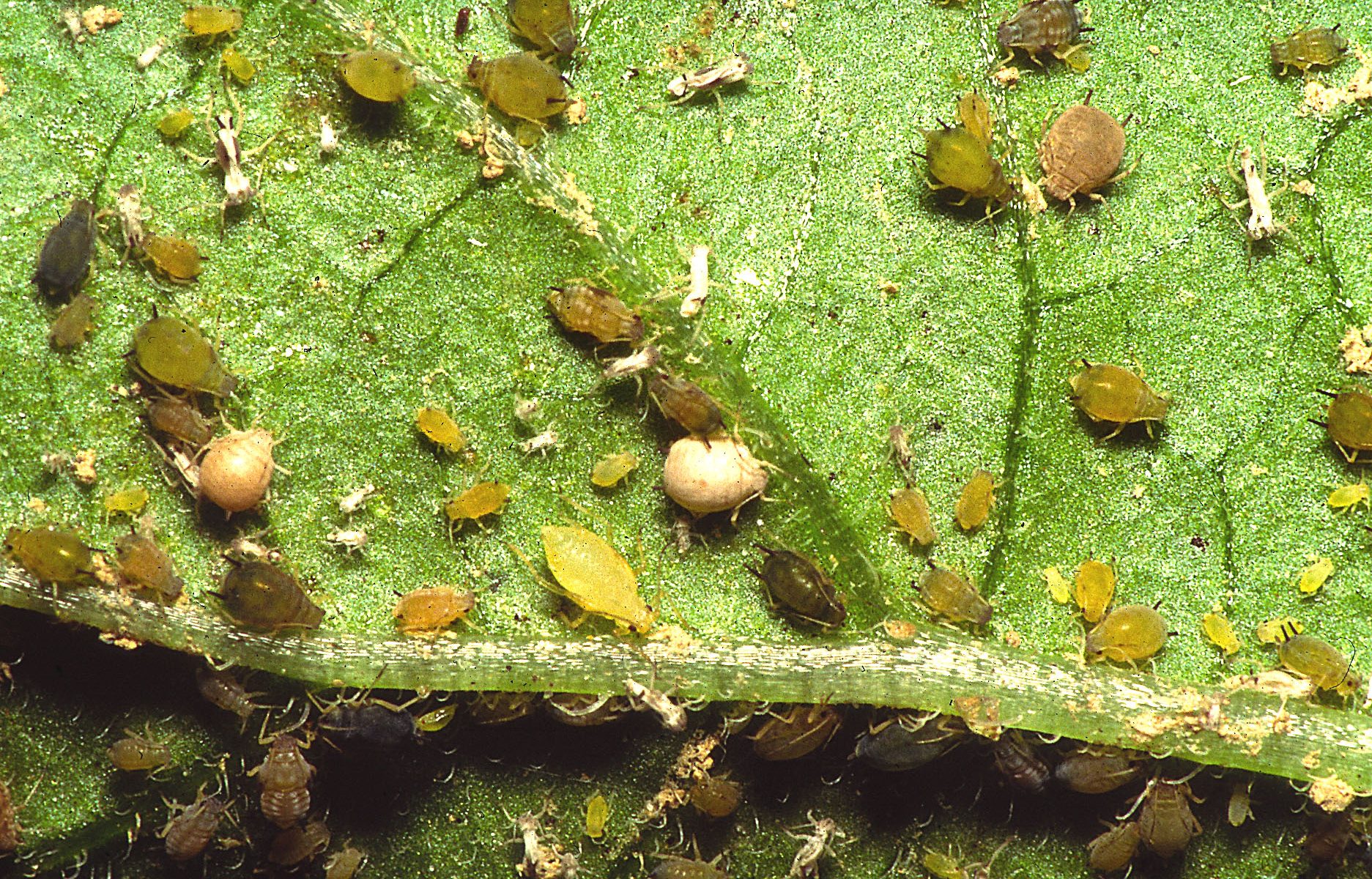
ShareAphid of Cucumber
Nymphs and adults are both soft-bodied pear-shaped, blackish in colour.
- Large colonies of nymphs and adults are found on tender twigs and shoots as also on ventral leaf surface sucking the vital sap from the tissues.
- The affected parts turn yellow, get curled, wrinkled and deformed in shape and ultimately dry and die away.
- Fruit size and quality is also reduced.
- The aphids also exude copious quantity of honeydew on which sooty mould develops, in turn, hinder the photosynthetic activity of the vines, resulting in stunted growth.
- The fruits covered by sooty mould look unattractive and lose their market value.
- Profenophos 50% EC @ 400ml/acre OR
- Acetamipride 20 % SP 40-80 gm/acre OR
- Acephate 50% + Imidacloprid 1.8% SP @ 300 gm/acre
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
ShareControl of Fusarium Wilt in Gram
Control of Fusarium Wilt in Gram:- Wilt in chickpea (Gram) caused by Fusarium oxysporum fungi. Warm and humid environment is favourable for it. the prevention of the disease, the following precautions have to be taken.
- Conserved soil moisture during Monsoon.
- Level up after deep ploughing (6-7 inch).
- Use disease-free seed.
- Follow 6-year crop rotations.
- Grow resistant varieties.
- Seed treatment with Carboxin 37.%+ Thiram 37.5% @ 2 gm /kg or Trichoderma viride @ 5 gm/kg.
- Avoid sowing when temperature are high. Sown in second and third week of October.
- Irrigation in November-December.
- Apply Mycorrhiza @ 4 kg/acre at 15 days after sowing.
- Spraying Thiaphanate methyl 75% WP @ 300 gm/acre at before flowering.
- Spraying Propiconazole 25% EC @ 125 ml/acre at pod formation stage.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
ShareSoil Preparation for Potato Cultivation
Soil Preparation for Potato Cultivation:-
- A well pulverized seed bed is required for good tuberisation of potato crop.
- Potato is taken as a Rabi Crop. Soon after the harvest of Kharif Crop, the field should be Ploughed once 20-25 cm. deep with soil turning plough.
- Thereafter, two to three cross harrowing or four to five ploughings with local plough should be done.
- One or two plankings are also needed to make the surface smooth and leveled.
- Enough moisture is essential at the time of sowing.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
ShareWhy & how to apply FYM in soil?
-
Most of the arable lands across the country show low levels of organic carbon with deficiencies ranging from 11% to 76%.
-
FYM is a good source of organic carbon.
- Soil organic carbon is the key factor of soil fertility by releasing the nutrients for plant growth, promotes the structure of the physical and biological health of the soil.
- Farmyard manure is organic matter used as fertilizer in agriculture. Manures improve the fertility of adding organic matter and lots of nutrients, On average well-composted farmyard manure contains 0.5% N, 0.2 % P2O5and 0.5 % K2O.
- They supply plant nutrients including micronutrients and increase their availability.
- They improve soil physical properties like Water holding capacity, Porosity, etc.
- Heat and CO2 control harmful fungus & insects in the soil. This CO2 & Heat are released due to the decomposition of FYM.
- The nutrients are lost due to leaching by rainwater so 8 -10 Tones /acre well-rotted farmyard manure (FYM) should be spread uniformly on the unploughed soil.