- Use disease free certified seed.
- Do not grow pea for at least two years in the same land that has carried on infected crop.
- Remove and destroy the disease infected pea plants to check the spread of disease.
- Treat the seeds with carboxin 37.5 +thiram 37.5% @ 2.5 gm / kg seed.
- Weekly Spray Kasugamycin 5% + Copper Oxychloride 45% WP 320 gm/acre or
- Spray kitazin 48.0 w/w 400 ml/acre.
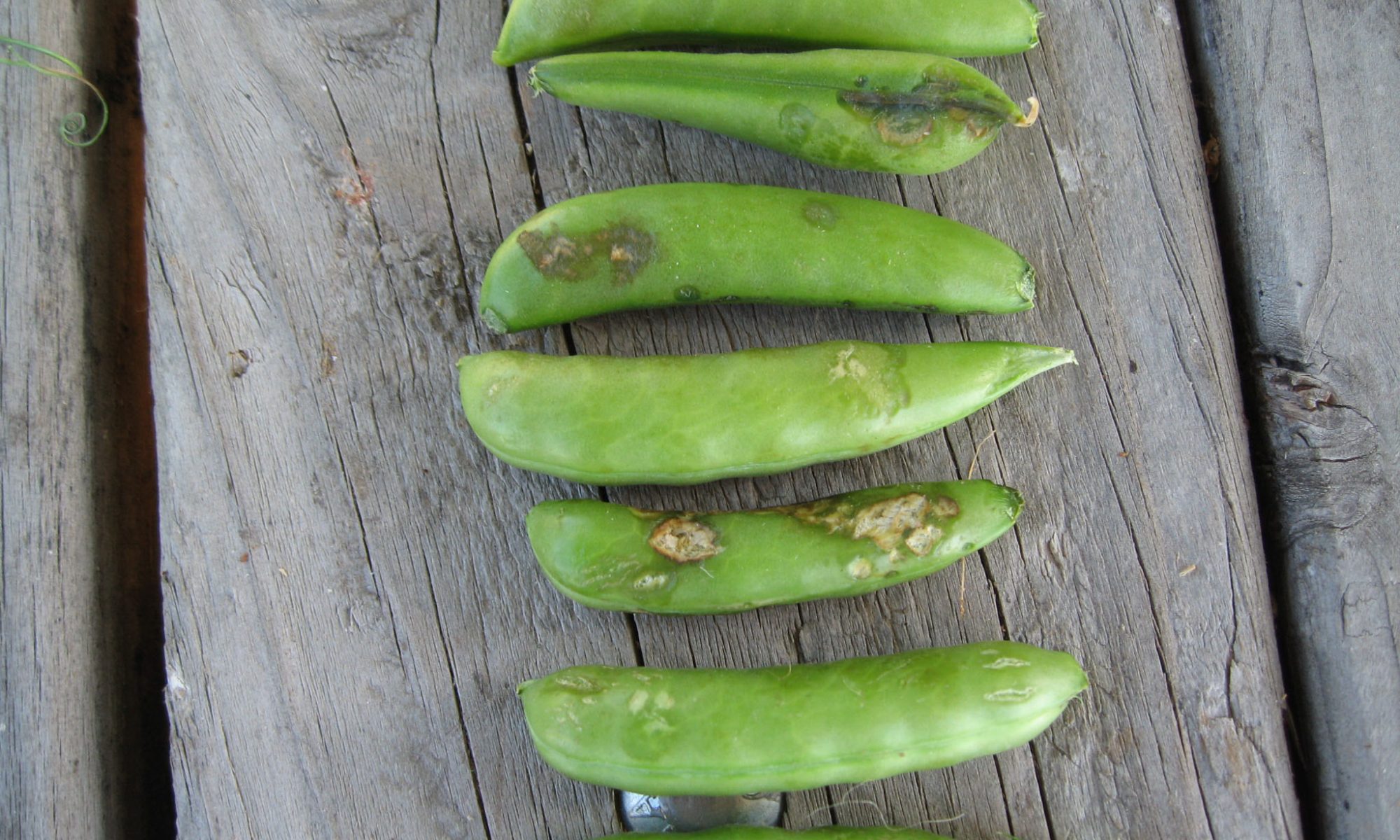
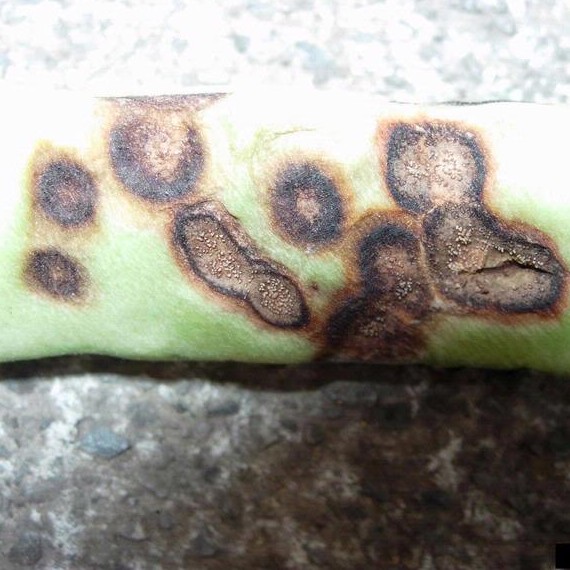
Identification of anthracnose disease on pea
- Leaves, stems and pods of pea are susceptible to infection.
- Small reddish-brown, slightly sunken spots form on the pods .
- These spots are rapidly developing into large, dark-sunken lesions on plants .
- In moist weather, masses of pink spores develop on these lessons.
- Infection of the leaves causes blacking along the veins particularly on the under surface.
Control of Blight and Foot Rot in Pea Crop
- Use healthy seeds and treat them with Carbendazim+Mancozeb @ 250 Gm/ quintals seed before sowing.
- Spray infected crop with Mancozeb 75% @ 400 gm/Acre at flowering and afterwards at 10-15 days intervals . or
- Spray infected crop with Thiophanate methyl 70% Wp @ 250 gram/acre.or
- Spray infected crop with Chlorothrlonil 75% WP @ 250 gram/acre.
- Remove diseased plants and destroy them.
- Maintain proper drainage.
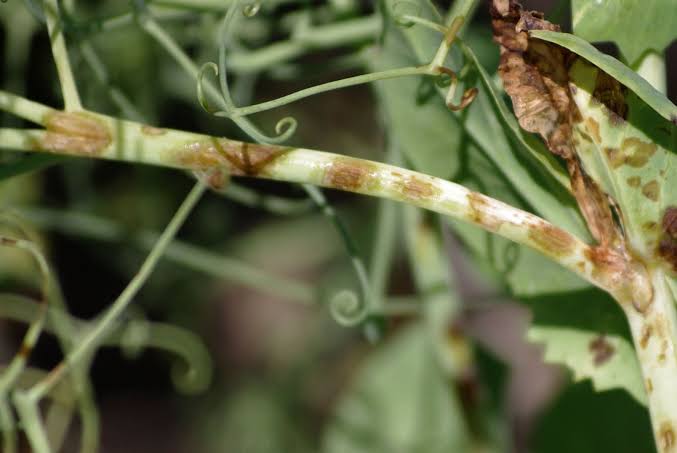
Identification of Blight and Foot Rot in Pea Crop
- Small, purple spots appear on leaves which may enlarge, turn brown and become zonate with a definite margin.
- Similar lesions also appear on the stem which elongate and coalesce causing browning or blackening of stem.
- On the pods, lesions are tan or brown in colour and irregular having a dark margin.
Control of Aphids in Pea
- Small green insects, adults are large pear-shaped green, yellow or pink in color.
Damage:-
- Suck the plant sap from leaves, flowers, and pods.
- The affected leaves often get cupped or become irregularly distorted, shoots become stunted and malformed.
- Honeydew secreted by the aphids encourages the growth of Sooty mold.
Requirement of Irrigation in Pea
- For proper germination, pre-sowing irrigation is a must if the soils are dry.
- Normally 2-3 irrigation is needed for midseason peas or late sown peas.
- Moisture stress at flowering and subsequent pod filling stage are most undesirable affecting the yield and quality of pods.
Grading of green peas
-
- When garden peas are intended for fresh market, it is necessary to remove over matured yellow pods, flat pods, the diseased and insect injured pods.
- Peas for processing are graded into four grades based on the size of shelled peas.
- Smaller sizes are considered to have the best quality.
Share
Harvesting of green pea
- Harvesting of green pods must be done at the proper stage.
- For the vegetable purpose, the pods are harvested when their color changes from dark green to light green and are well filled.
- The plant should be handled gently and if the vines are damaged during picking, the remaining pods will not develop properly.
Management of Wilt in Pea
- Treat seeds with Carboxin 37.%+ Thiram 37.5% @ 2 gm /kg or Trichoderma viride @ 5 gm/kg before sowing and avoid early sowing in badly infected areas.
- Follow 3 years crops rotation.
- Destroy the weed hosts.
- Apply Mycorrhiza @ 4 kg/acre at 15 days after sowing.
- Spraying Thiaphanate methyl 75% WP @ 300 gm/acre at before flowering.
- Spraying Propiconazole 25% EC @ 125 ml/acre at pod formation stage.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
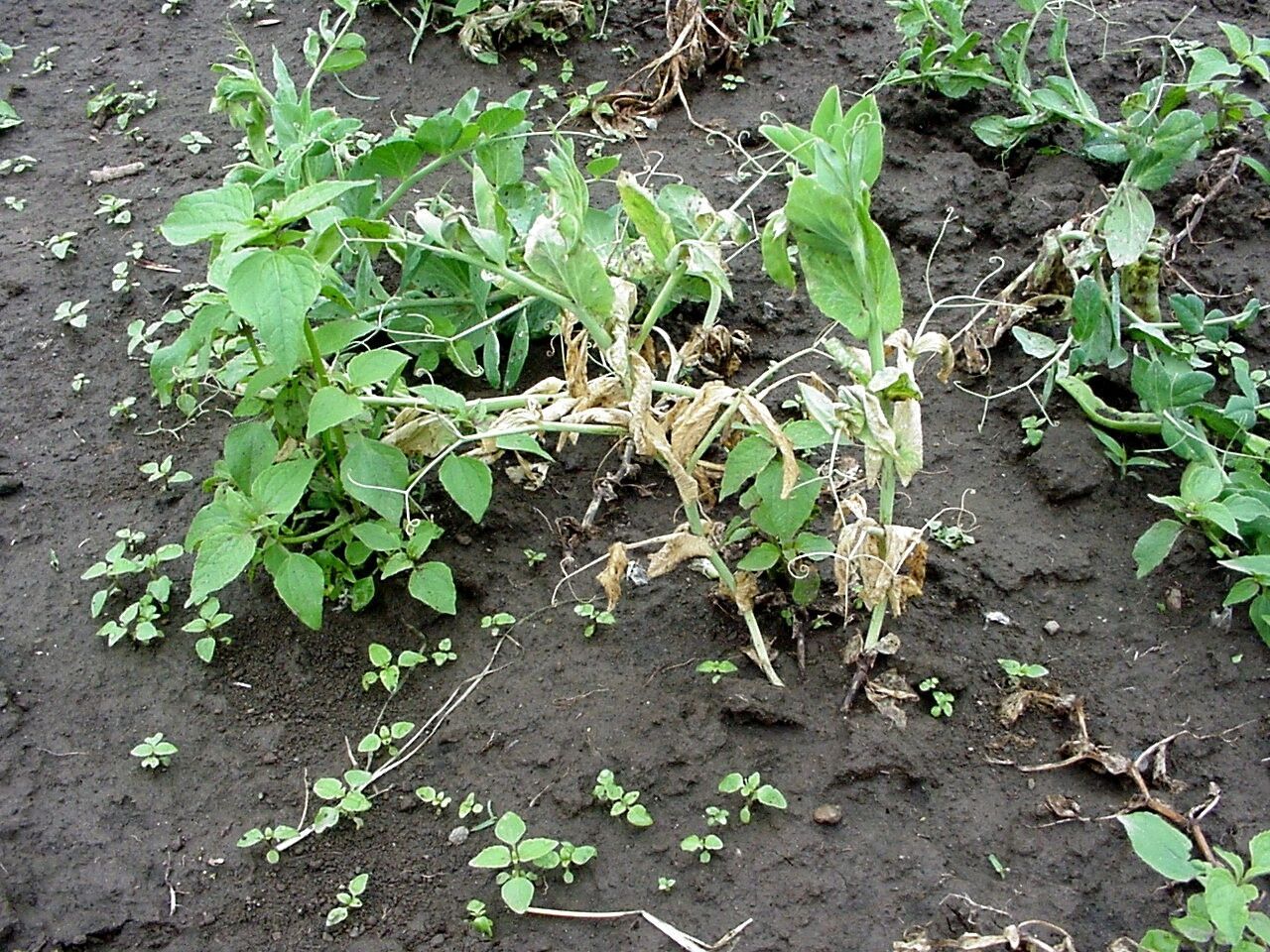
ShareSymptoms of Wilt in Pea
-
The roots turn black and the later rot away.
-
Plant growth is checked, foliage turn yellow and downward curling of stipules and leaflets takes place.
-
The entire plant wilts and the stem shrivels.