Role of Copper in Plant:- Copper is a highly essential component to healthy plant growth. Among other things, it plays a part in several enzyme processes and is key to the formation of chlorophyll.
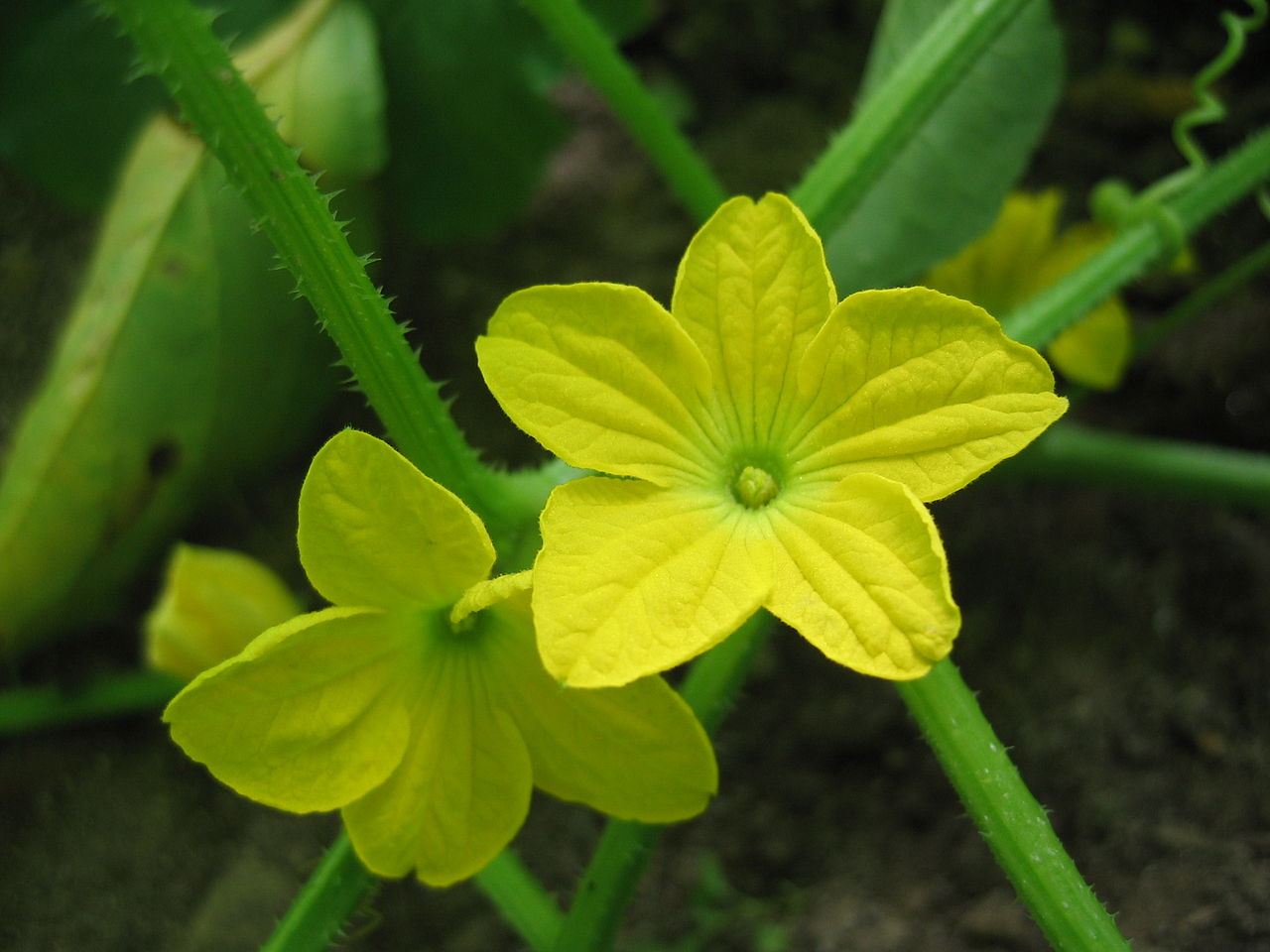
Function of Copper: Copper activates some enzymes in plants which are involved in lignin synthesis and it is essential in several enzyme systems. It is also required in the process of photosynthesis, is essential in plant respiration and assists in plant metabolism of carbohydrates and proteins. Copper also serves to intensify flavor and color in vegetables and color in flowers.
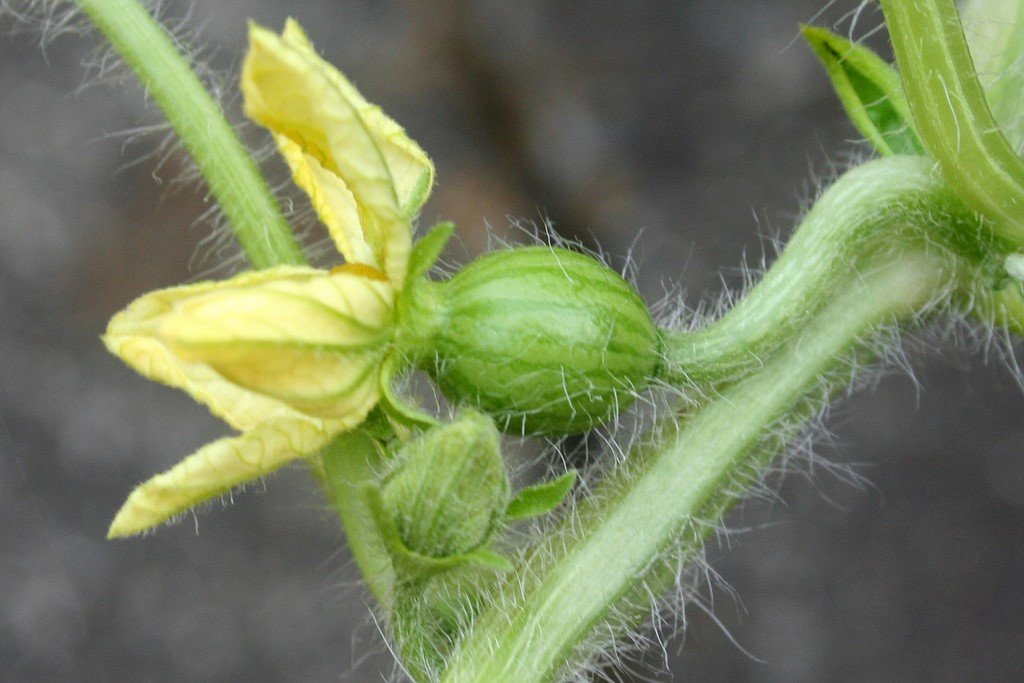
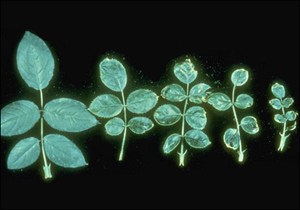
Deficiency: Copper is immobile, meaning its deficiency symptoms occur in the newer leaves. Symptoms vary depending on the crop. Typically, the symptoms start as cupping and a slight chlorosis of either the whole leaf or between the veins of the new leaves. Within the chlorotic areas of the leaf, small necrotic spots may form, especially on the leaf margins. As the symptoms progress, the newest leaves are smaller in size, lose their sheen and in some cases the leaves may wilt. The apical meristems may become necrotic and die, inhibiting the growth of lateral branches. Plants typically have a compact appearance as the stem length between the leaves shortens. Flower color is often lighter than normal.
Excess potassium, phosphorus or other micronutrients can indirectly cause copper deficiency. Also if the pH of the growing medium is high, this can induce a copper deficiency as it is less available for plant uptake.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
Share