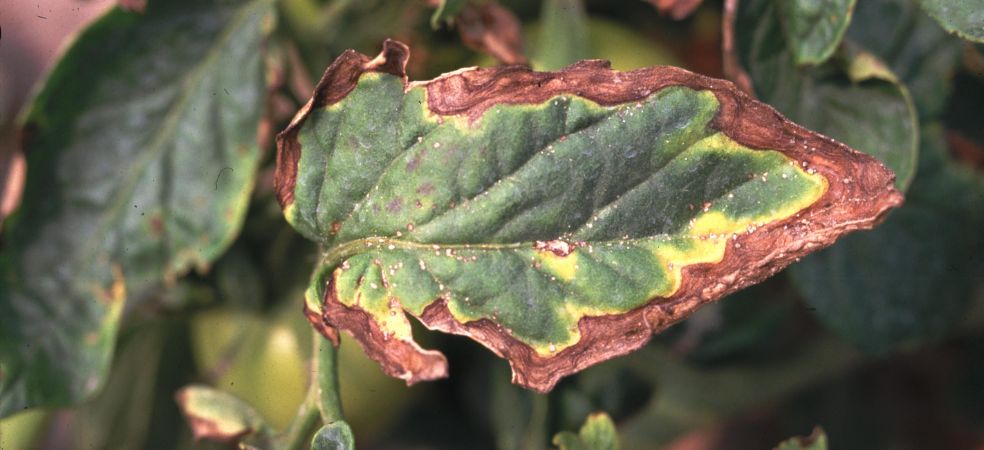
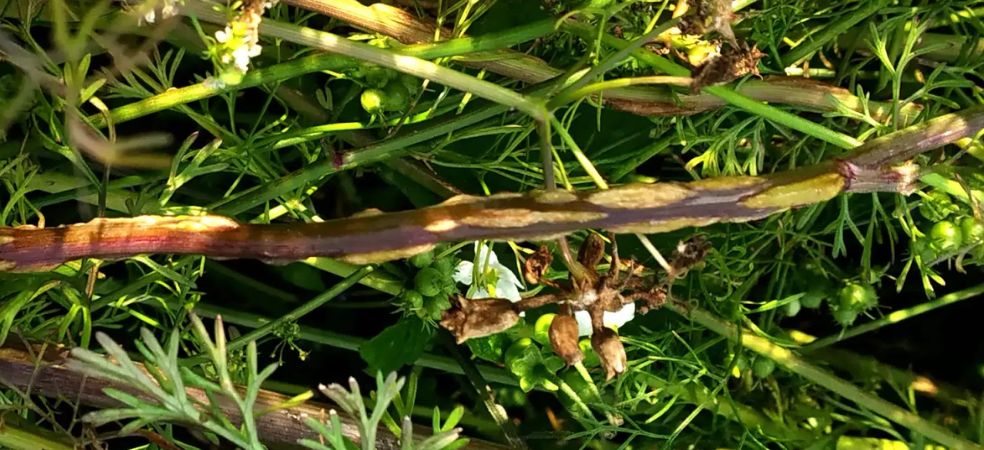
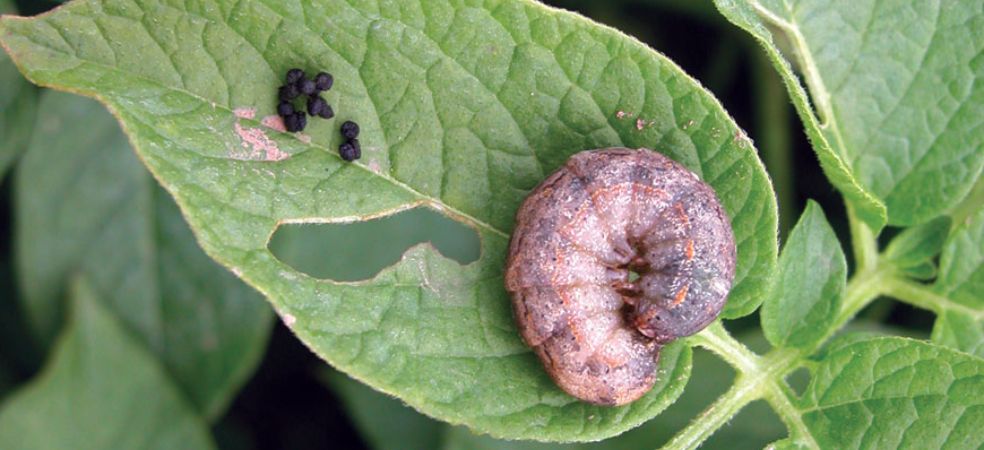
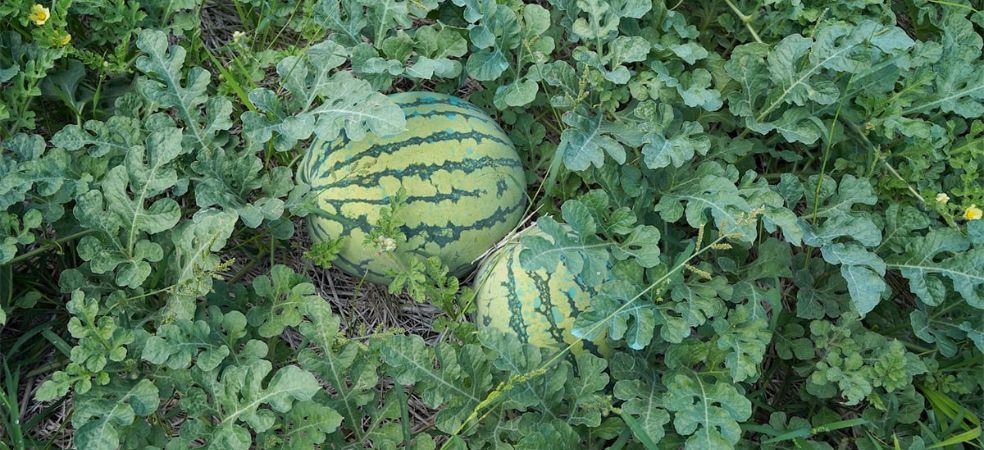
The bacteria of this disease are most active when there is moisture and light rain in the environment or in high humidity. Small, brown, water-soaked, circular spots with yellow circles appear on the leaves of affected plants. Older leaves start falling off and small, water-soaked spots appear on green fruits. The centre of these spots becomes irregular, light brown and with a scaly surface.
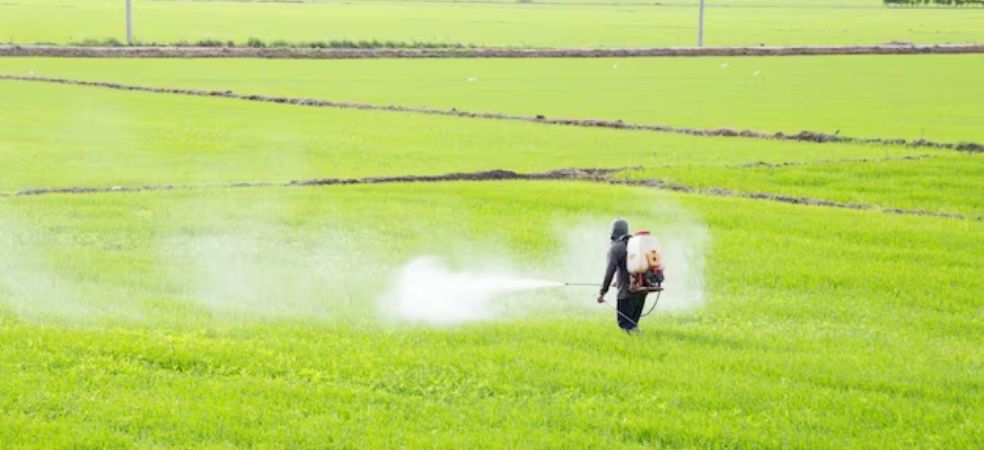
Control: To control this disease, spray Streptocycline (Streptomycin Sulphate 90% + Tetracycline Hydrochloride 10% SP) @ 20-24 gm per acre mixed with 150-200 litres of water as soon as the outbreak of the disease is observed.
ShareFor such important information related to the agriculture sector and farmers, do read Gramophone articles daily. If you liked today’s information then don’t forget to share it with friends.