-
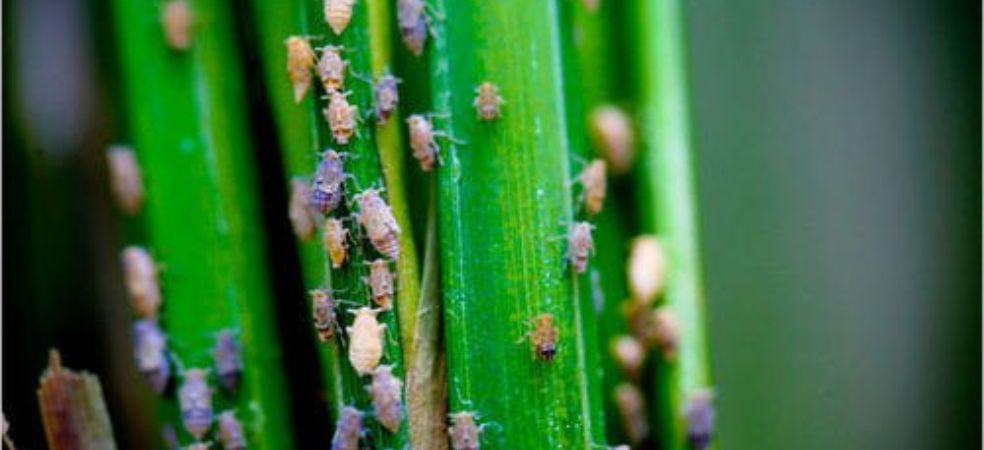
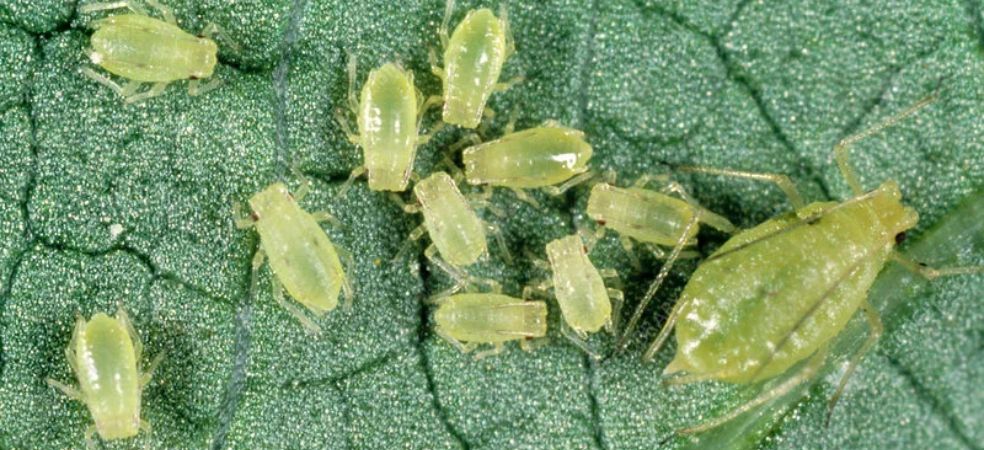
The adults of the brown plant hopper actually lay crescent-shaped eggs near the main veins of the leaves.
-
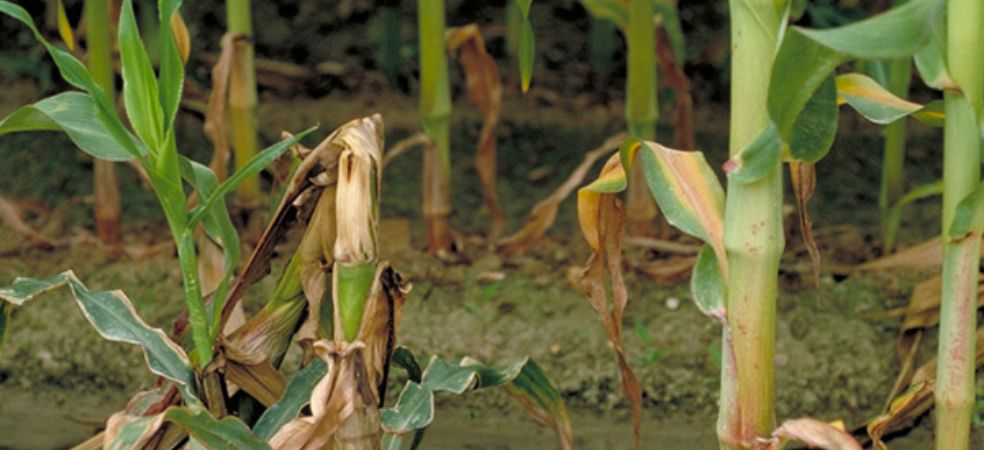
The nymph and adult of this insect are brown to white in colour and live near the base of the stem of the plant and from there, the plant gets damaged.
-
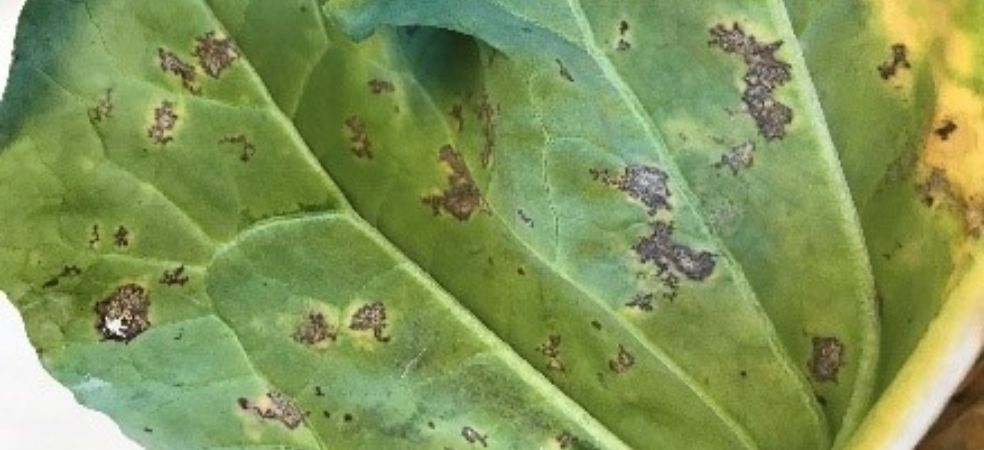
The damage done by plant hoppers is visible in the plant as yellowing.
-
Symptoms of hopper burn are seen when the population is high, in this situation 100 percent loss occurs from the crop.
-
For control of brown plant hopper in paddy, use Novaceta (Acetamiprid 20% SP) @ 40 gm/acre or Fipnova (Fipronil 5% SC) @ 400-600 ml/acre.
ShareFor such important information related to the agriculture sector and farmers, do read Gramophone articles daily. If you liked today’s information then don’t forget to share.