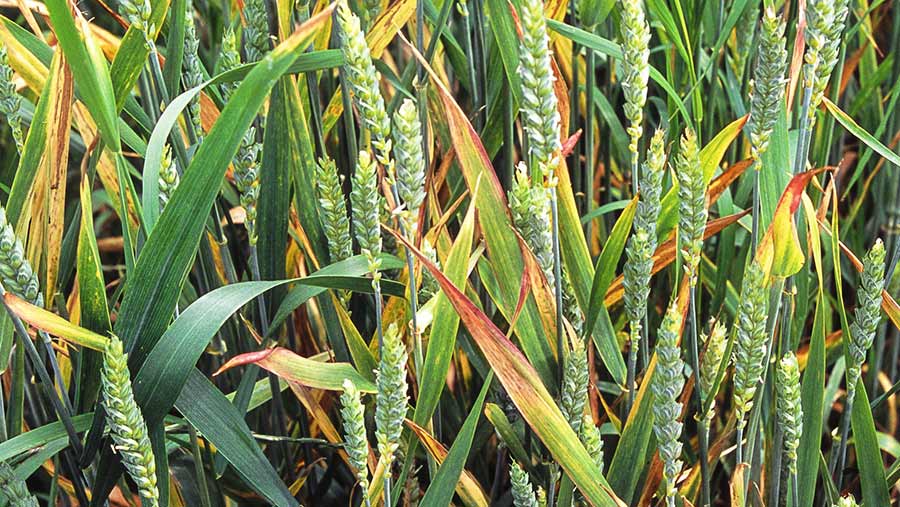
Rust is a major disease of wheat crop and there are 4 types of rust found in wheat i.e. Yellow Rust (Strip Rust), Leaf Rust (Brown Rust), Black Rust (Stem Rust).
Symptom-
- Yellow Rust (Strip Rust) :- Stripe rust is caused by the fungus Puccinia striiformis. It is easily distinguished from other wheat rusts by the orange-yellow spores, which produce small, closely packed pustules developing into stripes along the length of the leaf veins. The spores occur on the upper surface of the leaves, the leaf sheaths, awns and inside of the glumes.
-
Favorable Condition:- Stripe rust requires cool and wet conditions to infect the crop. Free moisture on the leaves and an optimal temperature (10-15°C) are required for infection. Pustules erupt within 10-14 days after infection. The disease can cause up to 25% yield loss.
-
Leaf Rust (Brown Rust):- Leaf rust is caused by the fungus Puccinia triticinia. The disease can also infect rye and triticale. Leaf rust produces reddish-orange colored spores that occur in small, 1.5 mm, circular to oval-shaped pustules. These are found on the top surface of the leaves, distinguishing leaf rust from stem rust which is found on both surfaces of the leaf.
- Favorable Condition:- The spores require 15 to 20º C temperature and free moisture (dew/rain/irrigation) on the leaves to successfully infect wheat. The first signs of the disease (sporulation) occur 10-14 days after infection. Removal of volunteer wheat plants, which forms a green bridge for the fungus through the summer, can eliminate or delay the onset of leaf rust.
- Black Rust (Stem Rust):– Stem rust is caused by the fungus Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. In addition to wheat, it can also attack barley, rye, and triticale. Stem rust produces reddish-brown spore masses in oval, elongated or spindle-shaped pustules on the stems and leaves.Unlike leaf rust, pustules erupt through both sides of the leaves. Ruptured pustules release masses of stem rust spores, which are disseminated by wind and other carriers.
- Favorable Condition:- Stem rust develops at higher temperatures than the other wheat rusts within a range of 18-30°C. Spores require free moisture (dew, rain or irrigation) and take up to six hours to infect the plant and pustules can be seen after 10-20 days of infection.
Management:-
- Destroy volunteer wheat plants.
- Crop rotation is very important in the case of the yellow spot.
- Growing resistant varieties is an economical and environmentally friendly way of disease reduction.
- During the growing season active crop monitoring is very important for an early detection of diseases.
- Avoid repeated use of fungicides with the same active ingredient.
- Spray Kasugamycin 5% + Copper Oxychloride 45% WP 320 gm/acre or Propiconazole 25% EC 240 ml/Acre.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
Share