Identification
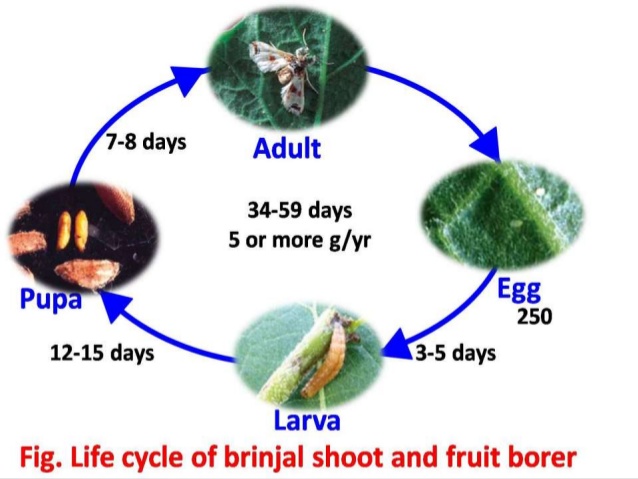
- The female moth lays eggs individually on the shoots of young brinjal plants.
- Creamy-white eggs are laid singly or in groups on the undersides of the leaves, stems, flower bunds or the base of the fruit.
- The young caterpillar id 15-18mm long, dull white and turns light pink as it matures.
- The adult moth is white with a pink or bluish tinge and brownish on its wings.
- The newly hatched larva prefers to bore directly into the fruit.
- When feeding is complete pupation occurs on stems, dried shoots, or among fallen leaves.
- Multiple over lapping generations occur in warm climates.
Damage
- The damage of the fruit starts soon after transplanting and continues till harvesting of the fruits.
- Short pinkish larva of the pest initially bore into the terminal shoots resulting in withering and drying of the shoot.
Control
- Continuous cropping of brinjal on the same piece of land should be avoided.
- Fruits showing boring should be picked and destroyed.
- Spray the crop with cypermethrin 25% EC (0.5ml/lit) or Cloropyrifos 20 % EC (4 mill ) of per litre water at fortnight intervals starting from 35 days after transplanting to control the pest.
- Best results are obtained when all the affected fruits are removed before spraying.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below.
Share