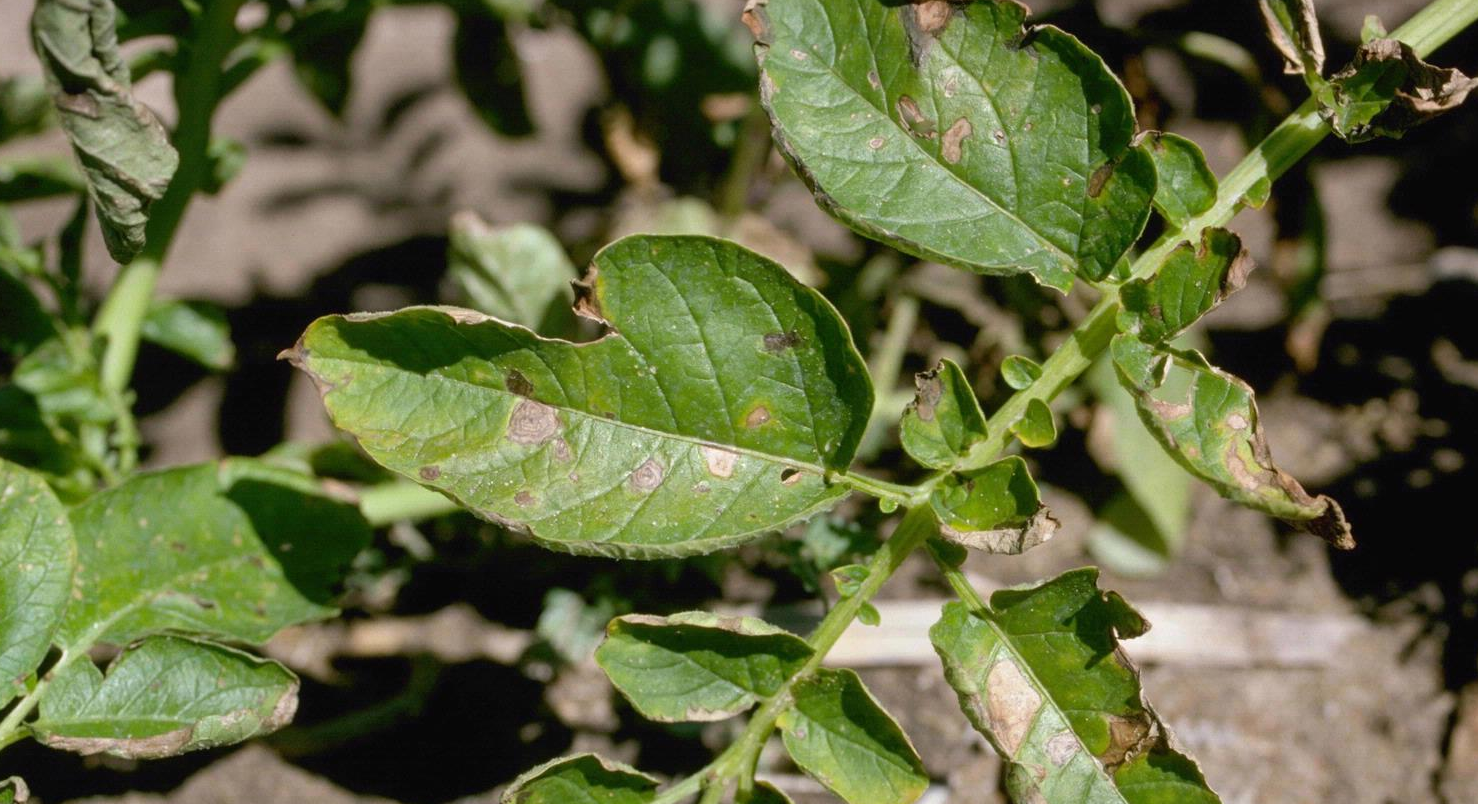
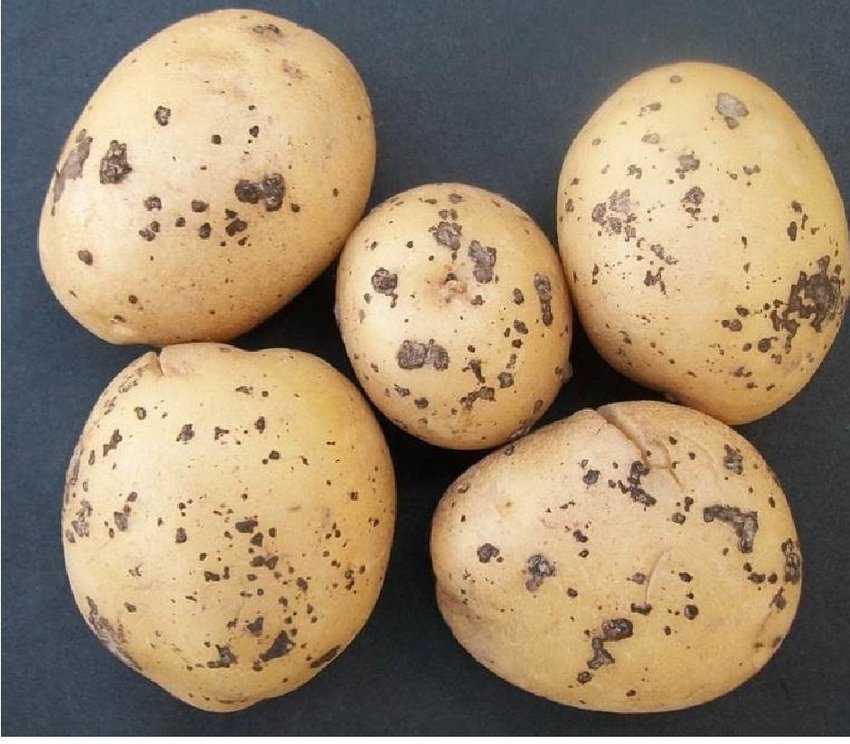
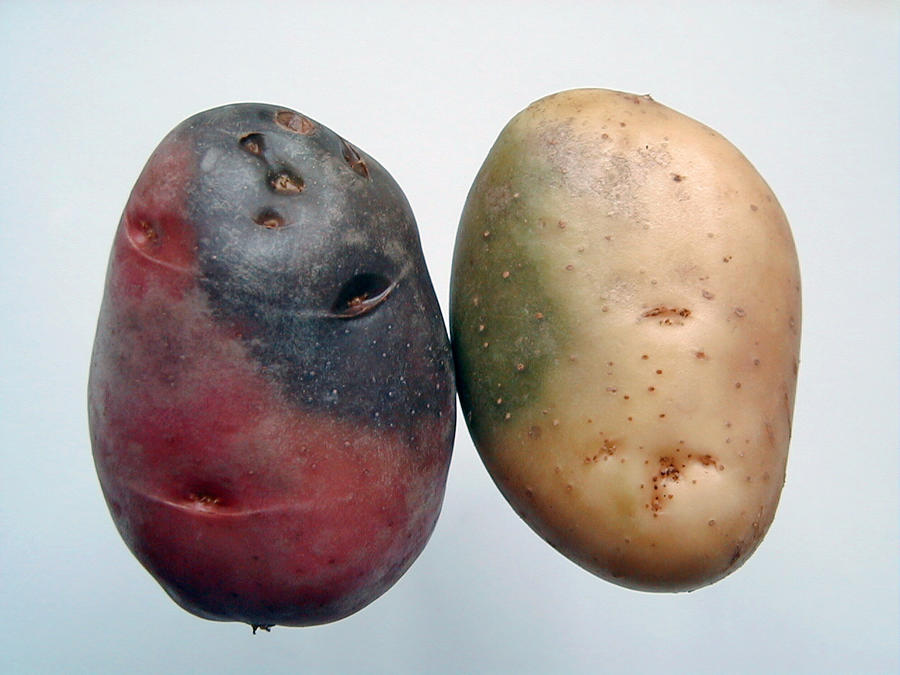
Spray any one fungicide for control of this disease
- Carbendazim 12%+ Mancozeb 63%@ 300 gm/acre.
- Thiophanate methyl 70% Wp @ 250 gm/acre.
- Chlorothrlonil 75% WP @ 250 gm/acre.
- Kasugamycin 5% + Copper Oxychloride 46% WP@ 300 gm/acre.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on the button below
Share