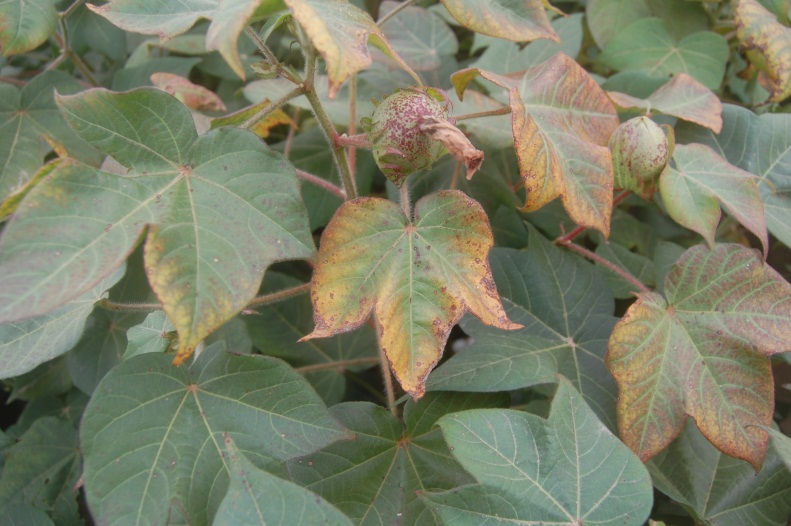
Potash deficiency and their control in Cotton :-
Prior to peak bloom, potassium deficiency in cotton presents itself as interveinal chlorosis on older leaves. These areas of interveinal chlorosis can progress to a red/gold color on these leaves followed by necrosis and/or the onset of foliage disease symptoms Due to potash deficiency, shading of leaves is observed also boll opening is not proper. Leaves get curled and become dry.
Control:- Spray Two to three times 00:52:34 or 00:00:50 @ 100 gm per pump.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
Share