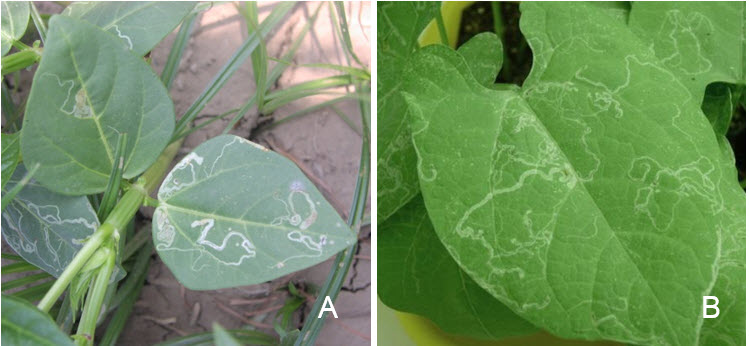
Identification:-
- Egg are 1 to 1.5mm long whitish in colour, elongate cylindrical in shape. Slightly curved and tapering at both ends.
- Full grown maggot are 5 to 10 mm. long cylindrical in shape, tapering an teriorly an blunt at posterior end and pole white in colour.
- Pupae are 5 to 8mm long, barrel shaped and brown to ochraceous in colour.
- Adult fly has reddish brown body with transparent and shiny wings. Bearing yellow- brown streaks.
- Adult fly are 4 to 5mm long having a wings expanse of 11 to 13 and 14 to 16mm in males and females respectively.
Damage:-
- The maggot burrow in to the fruits and suck the sap.
- Infested fruit decay and drop.
- The fly mainly prefers tender fruits for egg laying.
- Ovipositional punctures caused by adults also cause injury on fruits and fruit juice oozes out.
- This also results in distorted and malformed.
- The maggots feed on the pulp of fruits as well as on the immature seeds and cause premature dropping of fruits.
Control:-
- Collected and destroy infected fruits.
- To prevent egg laying fly traps (Pheromons traps) can be set up in the yield with 1%methyl Engenol or Cintronella oil or vinegar or dextrose or Acetic acid or laetic acid.
- Cover developing fruits with paper or polythene cover immediately after anthesis pollination.
- Maize plants grown in rows at a distance of 8-10cm in cucurbit field is effective as flies rest on such tall plants.
- Soil incorporation of cabaryl 10% dust can be made in fruit fly endemic areas.
- Spraying of Dichlorovas @3ml/lit of water at fortnightly intervals.
- Deep ploughing to expose hibernating stages.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below.
Share