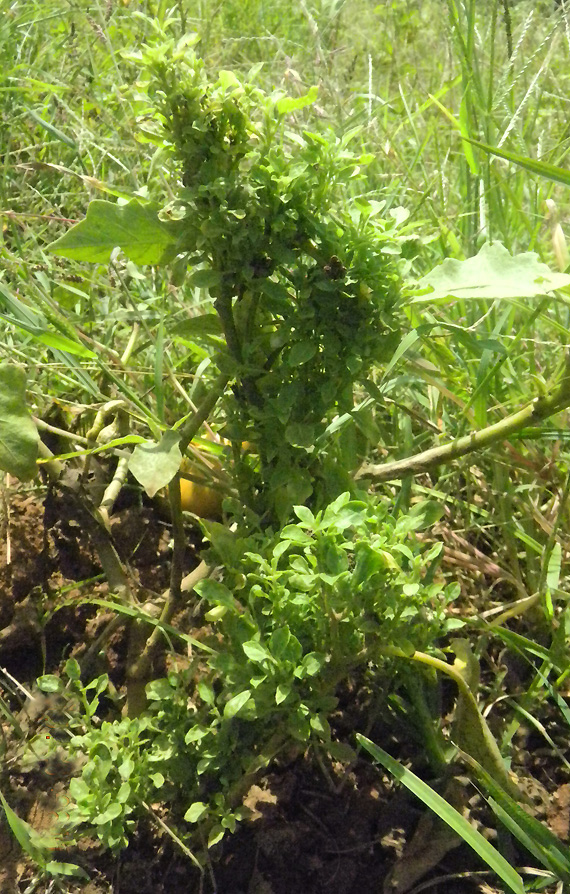
LITTLE LEAF IN BRINJAL
SYMPTOMS:-
- The leaves of the infection in the early stages are light yellow in colour.
- The leaves show a reduction in size and are malformed.
- Disease affected plants are generally shorter in bearing a large number of branches, roots and leaves then healthy plants.
- The petioles, axil of leaves and internodes get shortened thus giving the plants a bushy appearance.
- Flower parts are deformed leading the plants to be sterlile.
- Infected plants do not bear any fruits.
CONTROL:-
- Use barriers of trap crops.
- Remove and destroy infected plants.
- The sowing time can be adjusted to avoid the main flight of the beet leaf hopper.
- Spraying of Dimethoate 2ml per litre of water has been recomended for vector control.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below.
Share