Control of Gram pod borer in Soybean
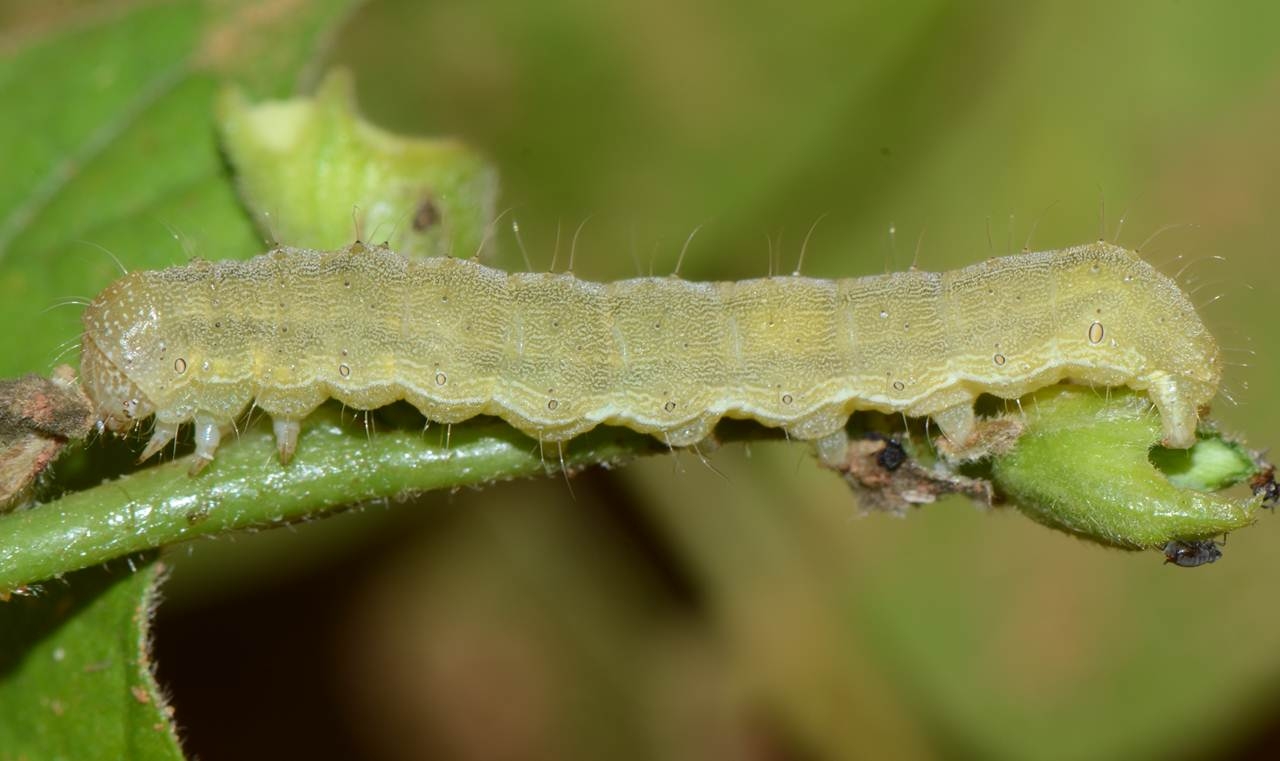
Symptoms of damage:-
- The young larvae feeds on the chlorophyll of young leaves and skeletonize it.
- They feed voraciously on the foliage in early stage,may defoliate the plant and later they feed on flowers and pods.
Management:-
- Deep summer ploughing
- Install pheromone traps at a distance of 50 Meter @ 5 traps/ha for each insect pest.
- Clip terminal shoots on 100 days of crop growth.
- Spray with Chloropirifos 20% EC @ 750 ml/acre or Quinolphos 25% EC @ 250 ml/acre
- Spray Deltamethrin 2.8% EC @ 250 ml/acre or Flubendiamide 20% WG @ 100 gm/acre
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
Share