- Spray Confidor(Imidacloprid) @ 100 ml + 250 gram beauveria bassiana/acre or
- Spray Thiamethoxam 12.6% + Lambda Cyhalothrin 9.5% ZC @ 100gm/acre or
- Spry acetamiprid 20% SP @ 40-80 gm/acre
- pick the aphids from the plant by hands or remove infected plant parts.
- Do not over-water or over-fertilize the crop.
Identification of Aphid in moong crop –
- Severe infestation can cause leaves and shoots to curl, wilt and stunted plant growth.
- The honeydew secreted by the aphid after secretion causes many fungal diseases on plants.
- The development of mould on the leaves indicates this problem.
- Dry and warm climates are optimal for the growth of aphids.
Controlling leaf miner can increase production in melon crop
- Affected plants during the growing season to be withdrawn and destroyed.
- Spray Wapkill (Acitamprid) @ 100 gm/acre or
- Confidor(Imidacloprid ) @ 100 ml + 250 gram beauveria bassiana/acre or
- Spray Thiamethoxam 12.6% + Lambda Cyhalothrin 9.5% ZC @ 100gm/acre or
- Spray Abacin (Abamectin 1.8% EC) @ 150 ml/acre
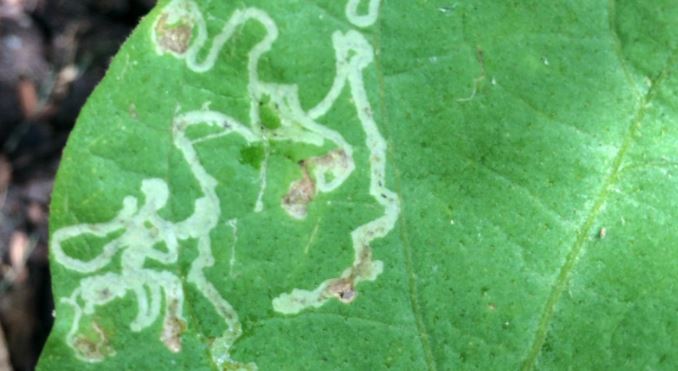
Identification of leaf miner on muskmelon crop –
- Adults leaf miners look like small black and yellow flies.
- Larvae exit from the leaf after completion of their development and then pupate axles on plants.
- Females puncture the leaf to feed plant sap and lays eggs within the leaf tissue.
- This damage restricts the plant growth and results in reduced bulb yield and loss of vigour.
- Tunnels or mines can be seen in the leaves.
How to manage fruit flies in cucurbits crops.
- Collect and destroy infested fruits.
- Flytraps (pheromone traps) can be set to prevent egg-laying by fruit flies.
- Maize plant s grown in the field are effective as flies rest on such tall plants.
- Deep ploughing should be done to expose hibernating stages of fruit flies.
- spray dichlorvos 76% EC 250 to 500ml/acre or
- Lambda Cyhalothrin 4.9% CS @ 200 ml/acre. or
- Profenofos 40%EC + Cypermethrin 4 %EC @ 400 ml/acre
Identification of fruit fly on pumpkin
- The worm bores into the fruits and sucks the sap.
- Infected fruits fall after decaying.
- These flies prefer tender fruits for egg-laying.
- The fly bore a hole into the fruit to lay her eggs inside it. Fruit Juice can be seen coming out from these holes.
- This also results in distorted and malformed.
- The maggots feed on the pulp of fruits as well as on the immature seeds and cause premature dropping of fruits.
How to treat Alternaria leaf blight in bottle gourd
- Adopt clean cultivation and crop rotation cultural practices to prevent this disease.
- Spray Mancozeb 75% WP at the rate of 400 gram/acre or
- Spray kitazin 48.0 w/w @ 400 ml/acre at 10-15 days intervals.
- Spray chlorothalonil 75% WP @ 300 gram/acre at 10 days intervals.
How to identify Alternaria leaf blight in bottle gourd?
Alternaria leaf blight in bottle gourd can be identified by the following symptoms-
- In the initial stages of this disease, Yellow spots appear on the leaves which then turn brown and finally turn black on ageing.
- They usually start from margins and then produce concentric rings.
- Severely affected vines start looking like burnt charcoal.
Importance of Soil testing in farming
Soil testing is very necessary for increasing production of any crop. It helps in –
- Determining the exact amount of chemical fertilizers used in crops.
- In identifying the correct way of improving the alkalic and acidic land and making it fertile.
- To determine the compatibility of the land for cultivation.
Why Aloe Vera is considered healthy in the summer season
Aloe vera has many health advantages, especially in the summer season. Some of its major advantages are as follows.
- Aloe vera has the ability to fight cancer.
- Aloe vera acts as a natural laxative.
- Helps reduce blood sugar.
- Improves digestion by eliminating stomach diseases.