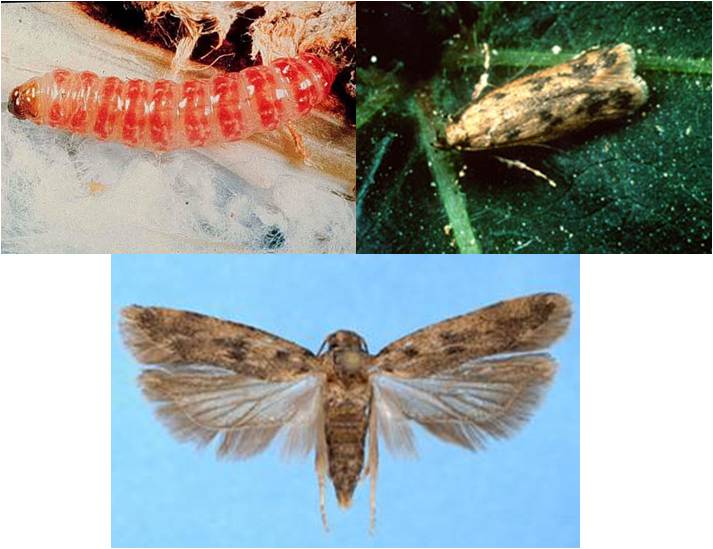
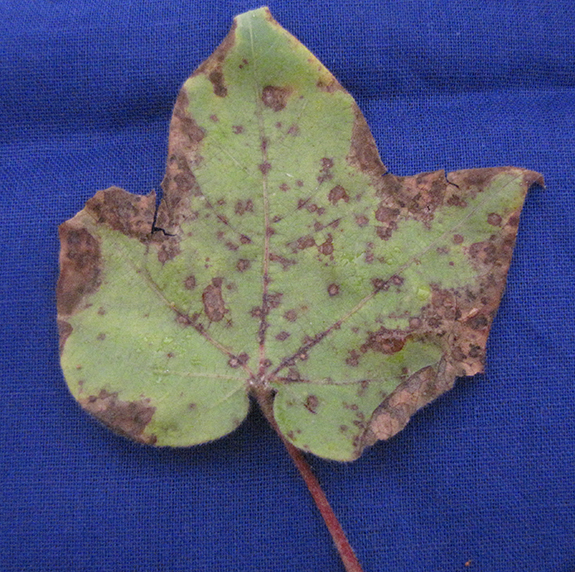
Control of White fly in Soybean :-
- Nymph and adults suck the cell sap from the leaves. The affected leaves curl and dry.
- The affected plants show stunted growth. White flies are also responsible for transmitting yellow vein mosaic virus or leaf curl disease.
- 3-4 foliar spray of Profenofos @ 50 ml/pump or Thaimathoxam @ 5 gm/pump or Acetamiprid 20% SP @15 gm/pump at 10 days interval.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
Share