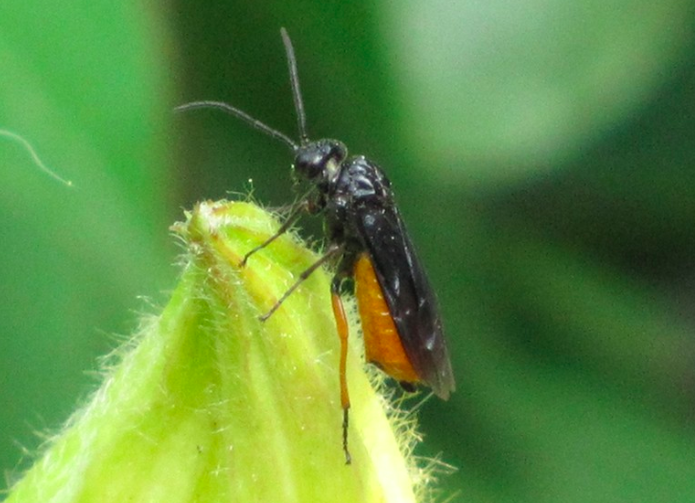
- The adult fly is orange colored with a blackhead.
- Mustard sawfly larvae feed on the leaves of rapeseed and mustard making holes. mustard sawflySometimes they eat up the entire lamina of the leaf leaving behind the midribs.
- It appears in the month of October and its peak season of activity is in November.
- The population disappears suddenly at the onset of winter.
Management of wheat head blast diseases
- Use disease-free certified seed.
- Remove and destroy the disease infected wheat plants to check the spread of disease.
- Treat the seeds with carboxin 37.5 +thiram 37.5% @ 2.5 gm / kg seed.
- Weekly Spray Kasugamycin 5% + Copper Oxychloride 45% WP 320 gm/acre or
- SprayThiophanate methyl 70% Wp 300 ml/acre.
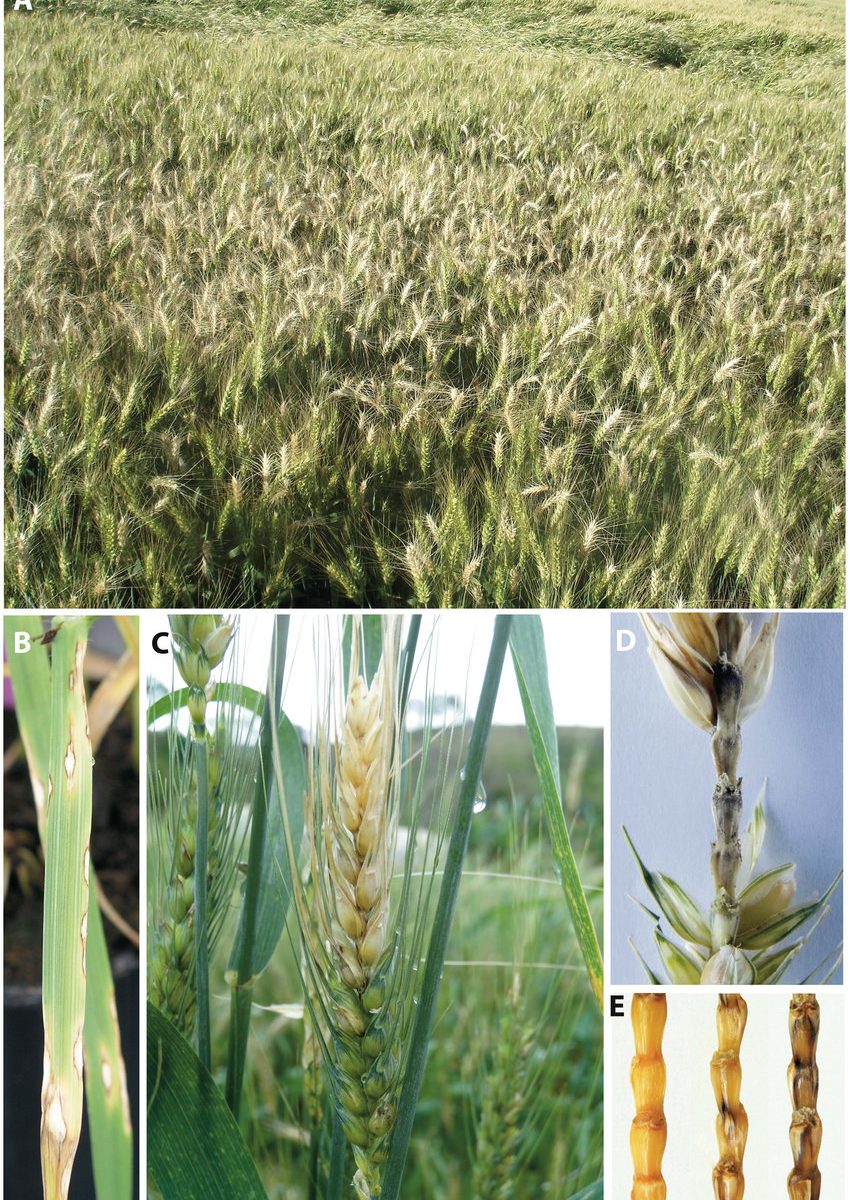
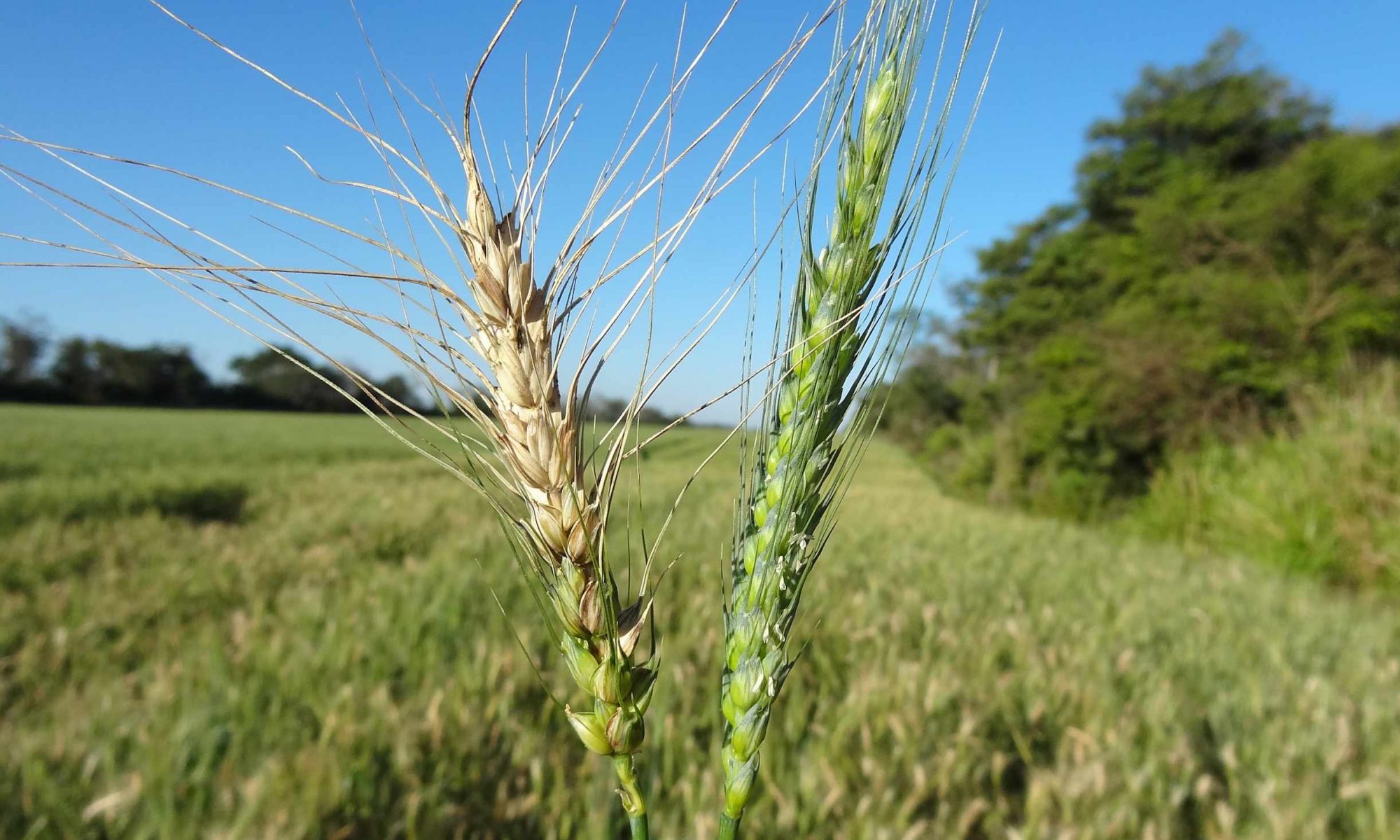
Identification of wheat head blast diseases
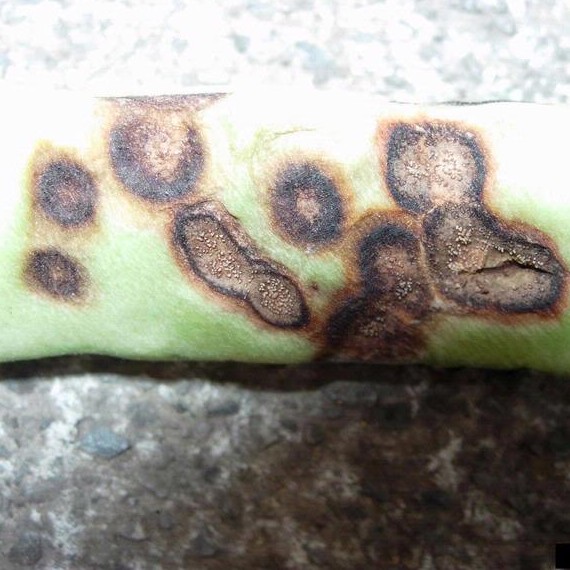
- Affected plants show typical eye-shaped lesions with light gray centers and dark brown spots on wheat leaves.
- The blast affected wheat spikes, with typical bleached head symptoms from the point of infection.
- complete bleaching of a wheat spike above the point of infection by blast fungus.
Management of anthracnose disease on pea
- Use disease free certified seed.
- Do not grow pea for at least two years in the same land that has carried on infected crop.
- Remove and destroy the disease infected pea plants to check the spread of disease.
- Treat the seeds with carboxin 37.5 +thiram 37.5% @ 2.5 gm / kg seed.
- Weekly Spray Kasugamycin 5% + Copper Oxychloride 45% WP 320 gm/acre or
- Spray kitazin 48.0 w/w 400 ml/acre.
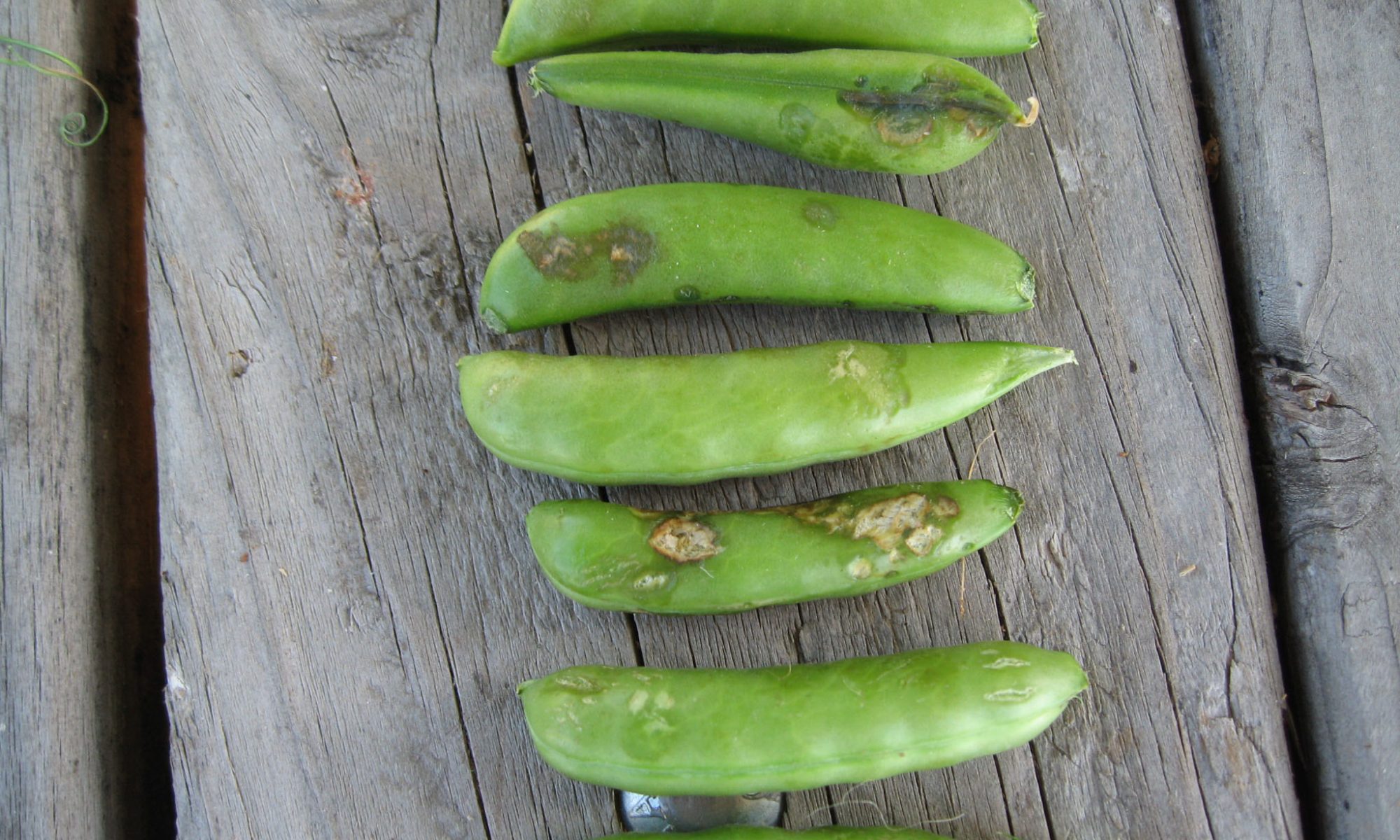
Identification of anthracnose disease on pea
- Leaves, stems and pods of pea are susceptible to infection.
- Small reddish-brown, slightly sunken spots form on the pods .
- These spots are rapidly developing into large, dark-sunken lesions on plants .
- In moist weather, masses of pink spores develop on these lessons.
- Infection of the leaves causes blacking along the veins particularly on the under surface.
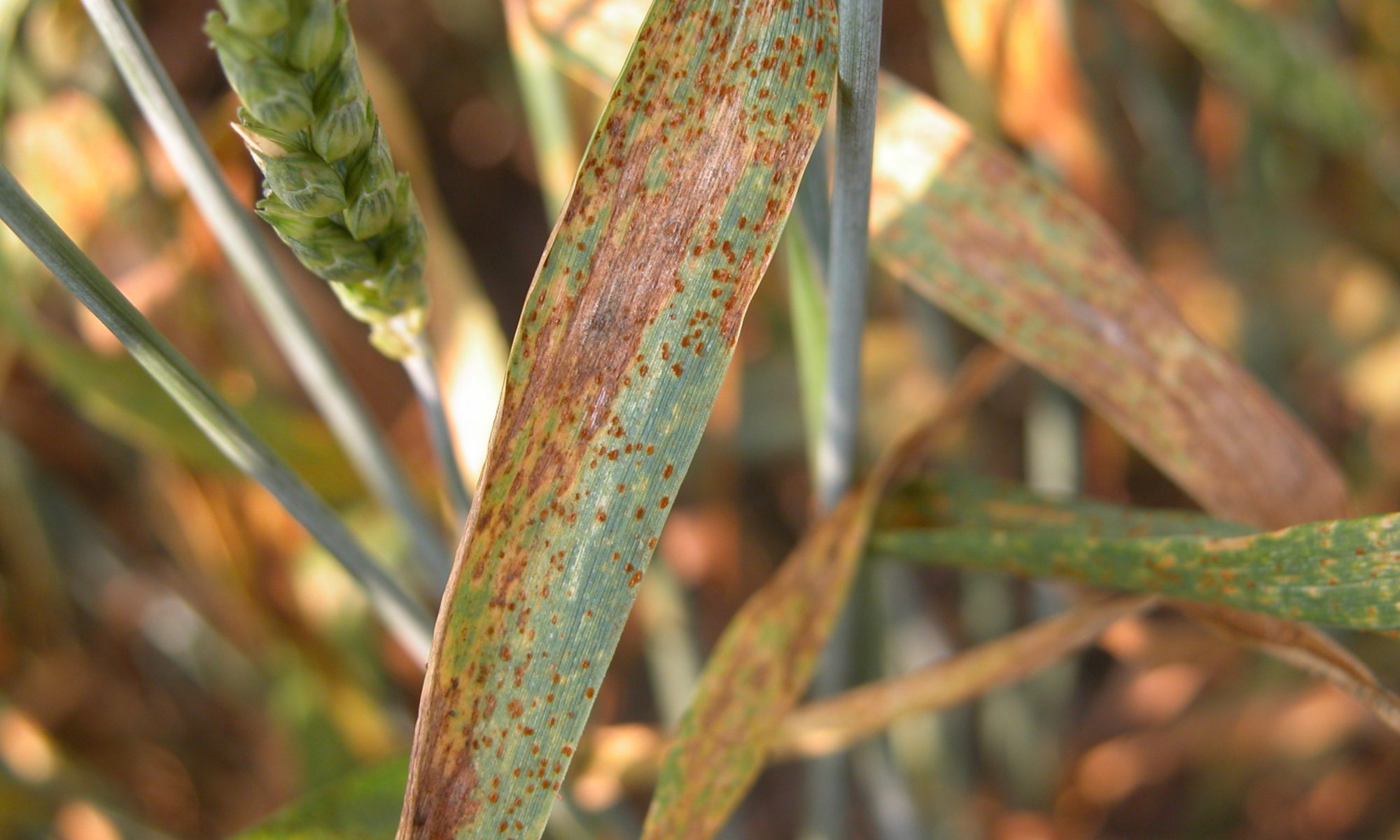
Management of Rust disease in Wheat
-
- Leaf rust is caused by the fungus.
- The first signs of the disease (sporulation) occur 10-14 days after infection
- Leaf rust produces reddish-orange coloured spores which occur in small, 1.5 mm, circular to oval-shaped pustules.
- These are found on the top surface of the leaves, distinguishing leaf rust from stem rust which is found on both surfaces of the leaf.
- The spores require 15 to 20ºC temperature and free moisture (dew/rain/irrigation) on the leaves to successfully infect wheat.
Management-
- Crop rotation is very important.
- Growing resistant varieties is an economical and environmentally friendly way of disease reduction.
- During the growing season, active crop monitoring is very important for an early detection of diseases.
- Avoid repeated use of fungicides with the same active ingredient.
- Spray Kasugamycin 5% + Copper Oxychloride 45% WP 320 gm/acre or Propiconazole 25% EC 240 ml/acre.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
ShareIdentification of wheat rust
- Leaf rust is caused by the fungus.
- The first signs of the disease (sporulation) occur 10-14 days after infection
- Leaf rust produces reddish-orange colored spores that occur in small, 1.5 mm, circular to oval-shaped pustules.
- These are found on the top surface of the leaves, distinguishing leaf rust from stem rust which is found on both surfaces of the leaf.
- The spores require 15 to 20ºC temperature and free moisture (dew/rain/irrigation) on the leaves to successfully infect wheat.
Application of Manure and fertilizers in Garlic
Garlic can be grown in almost all types of soil, however sandy, slit and clay loamy soil are best for cultivation, however it can also be grown in clayey soil. In heavy clay soil garlic should be planted in raised beds. Soil should be well drained and should be capable of holding water during the growth phase. Ideal pH should be 6 – 7.5 with high nitrogenous fertilizers @ 40 kg/.acre for early vegetative, phosphorus @ 20 kg/acre for better root development, potassium @ 20 kg/acre for critical leaf development and bulb formation. Pungency in garlic is because of good sulfur content. Sulfur should be given @ 20 kg/acre after plants have come out and leaf development has started for better pungency. Also mix the FYM at the @ 4-6 tonnes /acre at the time of preparation of the soil.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below.
ShareWeed management in Okra
- Apply deep ploughing before sowing.
- Follow Crop rotation, using such crop as grasses and small grains.
- Hand weeding 2-3 (20,40 and 60 days) after sowing.
- Spray of oxyfluorfen 23.5 EC @ 200 ml/acre at after sowing and pre-emergence.
- Spray of Pendimethalin 30% EC 700 ml/acre in three days after sowing.
- Spray of propaquizafop 10% EC 400 ml/acre at 2-3 leaf stage of weeds for the controlling of narrow leaf weeds.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
ShareNutrient management of Tomato
- Tomato needs a heavy dose of fertilizers for a good yield.
- Farmyard manure @ 8-10 tonnes/Acre may be incorporated into the soil one month before transplanting.
- DAP 50 kg/Acre, Urea 80 kg/Acre and MOP 33 kg/Acre.
- Full amount of DAP, MOP and half of Urea are to be added just before transplanting.
- Rest of the Urea is to be given as a second dose at 20-25 days after transplanting, and third dose is given at 45-60 days after transplanting.
- Zinc sulphate application (Znso4@10 kg/Acre) and Boron 4 Kg/Acre increases yield as well as improves the quality of fruit.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
Share