- Drain excess water
- Use resistant varieties: CO 439, CO 443, CO 720, CO 730 and CO 7704
- Spray THiamethoxam 25 % WP @1 00 gram 500 gram/acre.
- Spray thiamethoxam 12.6% + lambda Cyhalothrin 9.5% ZC @ + beauveria bassiana 500 gram/acre.
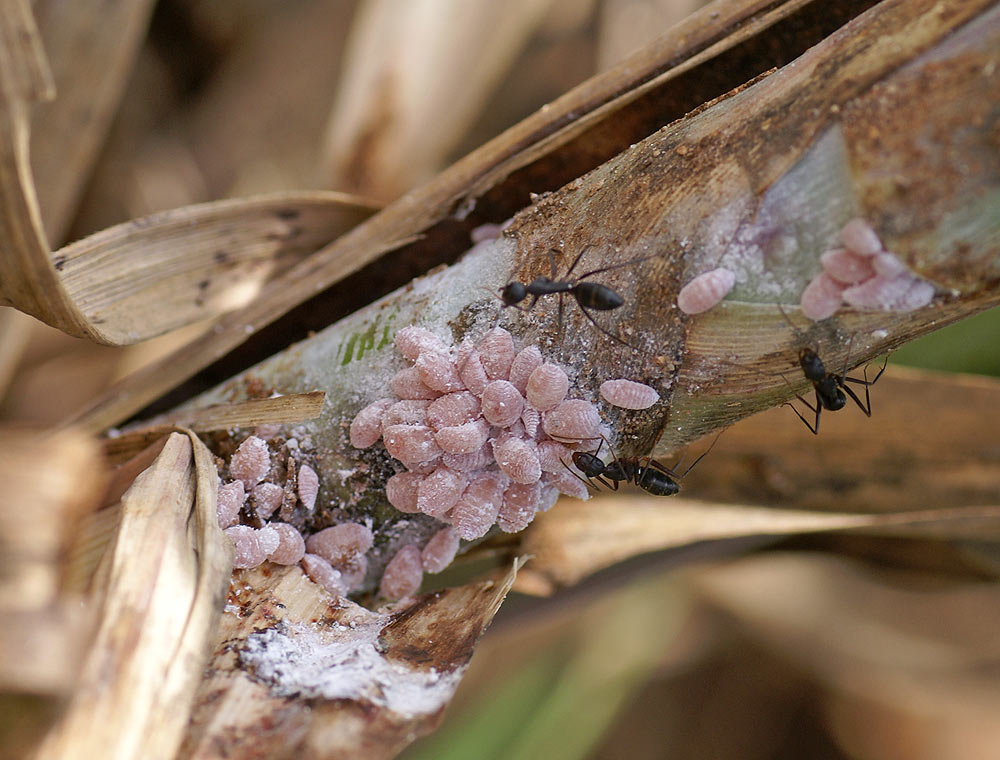
Identification of mealybug in sugarcane crop
- The mealybugs are pinkish with a white waxy covering and hundreds are found attached to the lower nodes of sugarcane under the leaf sheaths.
- Sooty mold develops on the honeydew giving a blackish appearance on canes.
- Severe attack results in stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, deposition of sticky honeydew, and development of sooty mould which lead to poor juice quality.
Chemical Management of mustard saw fly
- Spray Profenofos (celcron/carina ) @ 500 ml/ acre or
- Spray 12.6% + Lambda Cyhalothrin 9.5% ZC ( beleaf/alika) @ 80 gm/ acre or
- Spray Imidachloprid 30.5% SC (media super) @ 100 gm/ acre
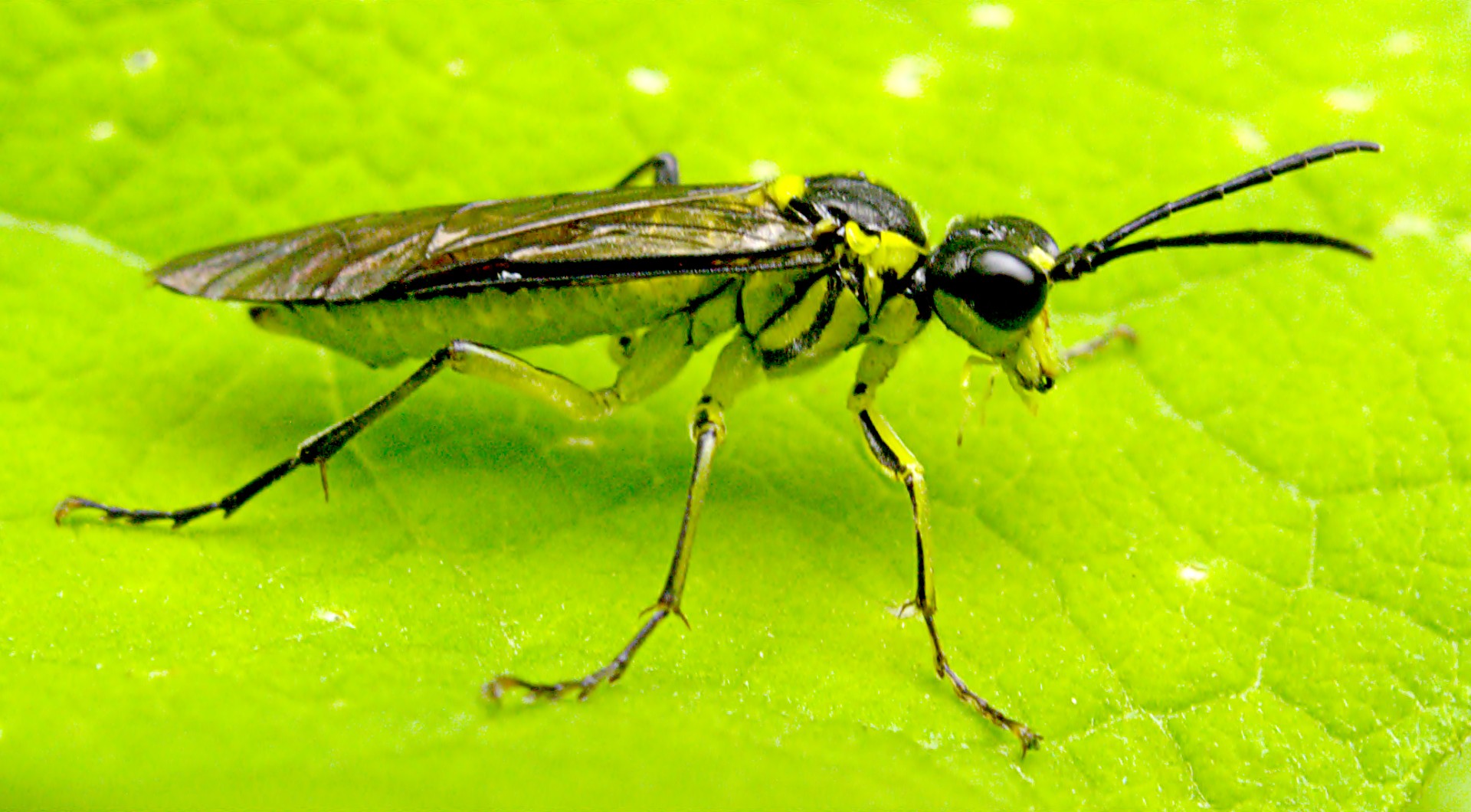
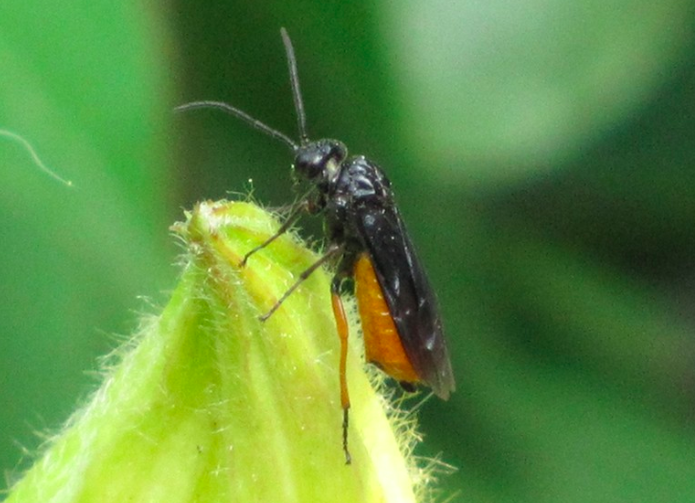
Identification of mustard sawfly
- The adult fly is orange colored with a blackhead.
- Mustard sawfly larvae feed on the leaves of rapeseed and mustard making holes. mustard sawflySometimes they eat up the entire lamina of the leaf leaving behind the midribs.
- It appears in the month of October and its peak season of activity is in November.
- The population disappears suddenly at the onset of winter.
Management of wheat head blast diseases
- Use disease-free certified seed.
- Remove and destroy the disease infected wheat plants to check the spread of disease.
- Treat the seeds with carboxin 37.5 +thiram 37.5% @ 2.5 gm / kg seed.
- Weekly Spray Kasugamycin 5% + Copper Oxychloride 45% WP 320 gm/acre or
- SprayThiophanate methyl 70% Wp 300 ml/acre.
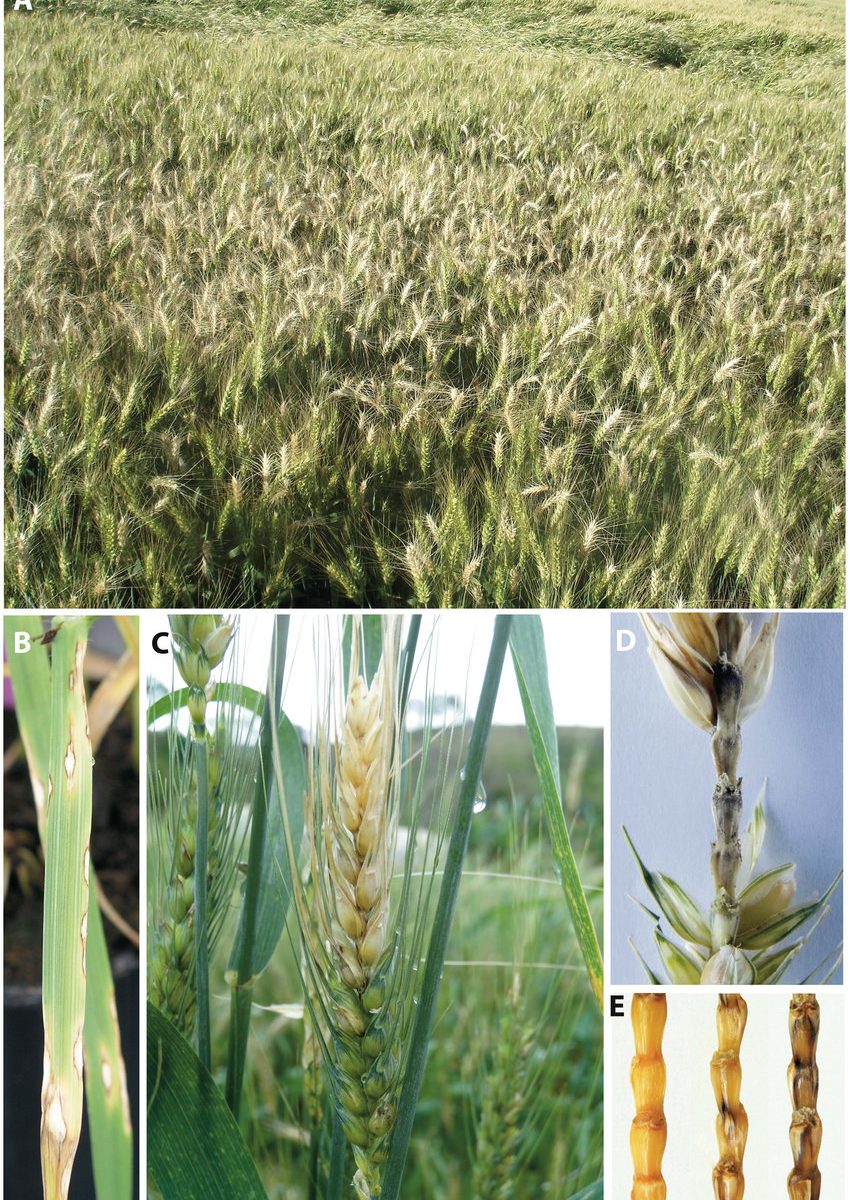
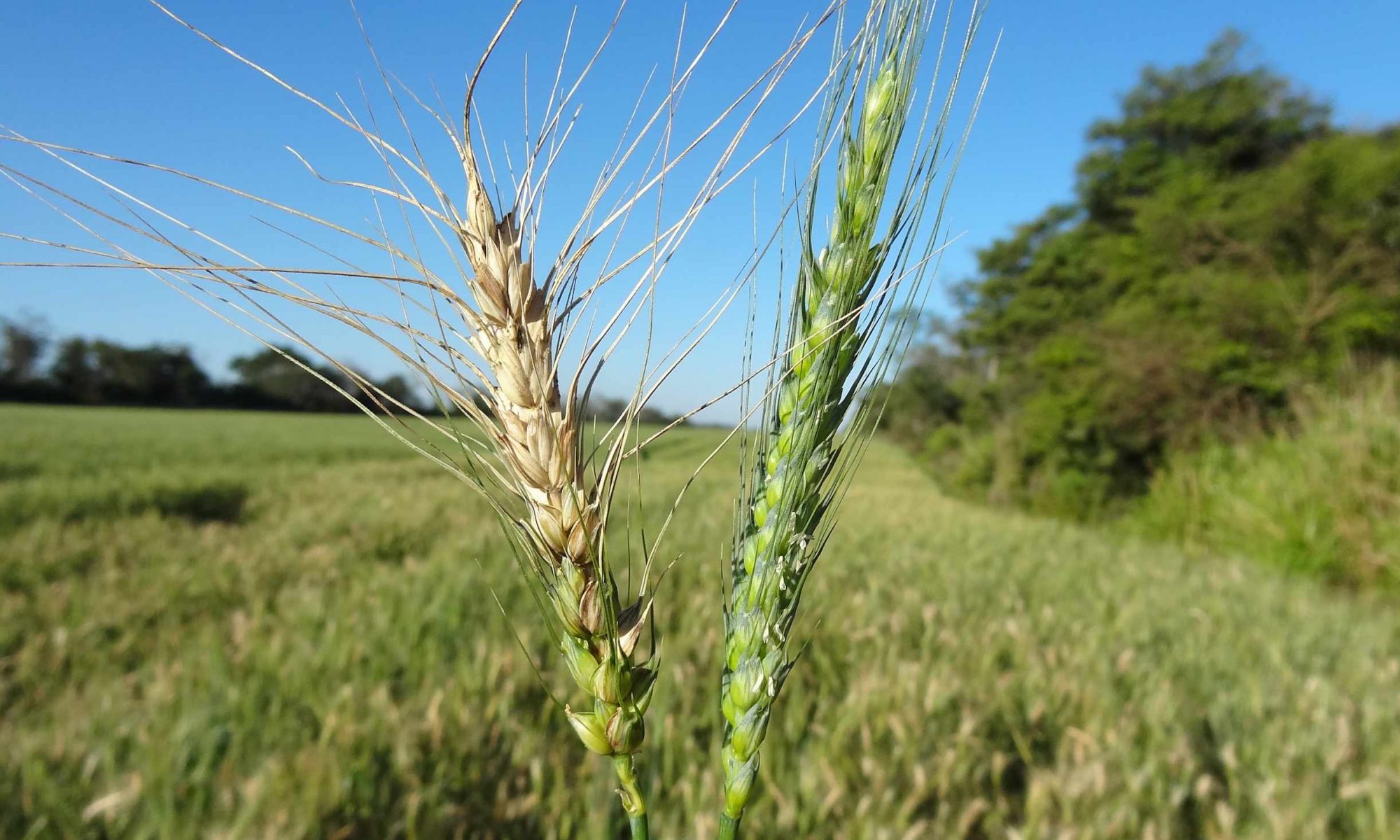
Identification of wheat head blast diseases
- Affected plants show typical eye-shaped lesions with light gray centers and dark brown spots on wheat leaves.
- The blast affected wheat spikes, with typical bleached head symptoms from the point of infection.
- complete bleaching of a wheat spike above the point of infection by blast fungus.
Management of anthracnose disease on pea
- Use disease free certified seed.
- Do not grow pea for at least two years in the same land that has carried on infected crop.
- Remove and destroy the disease infected pea plants to check the spread of disease.
- Treat the seeds with carboxin 37.5 +thiram 37.5% @ 2.5 gm / kg seed.
- Weekly Spray Kasugamycin 5% + Copper Oxychloride 45% WP 320 gm/acre or
- Spray kitazin 48.0 w/w 400 ml/acre.
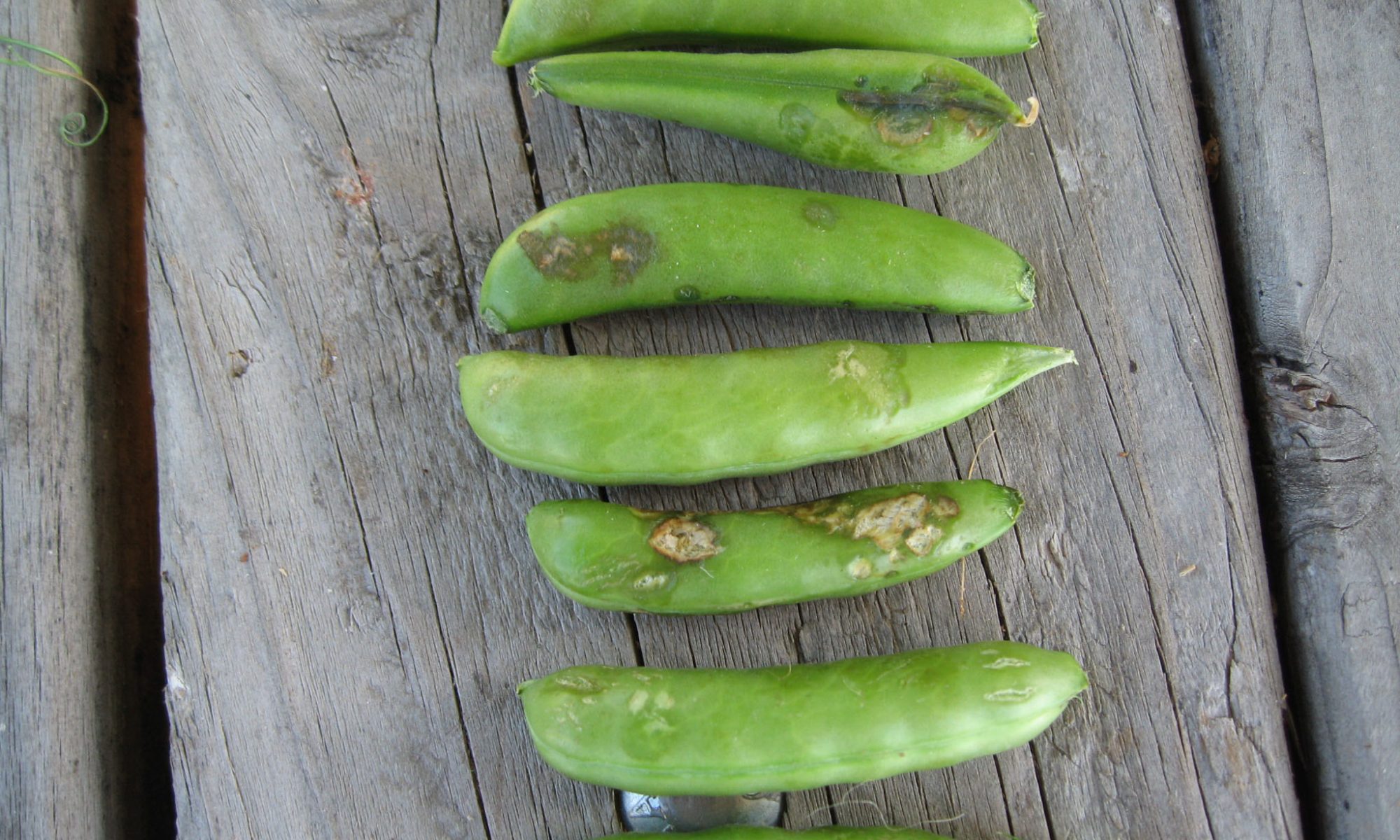
Identification of anthracnose disease on pea
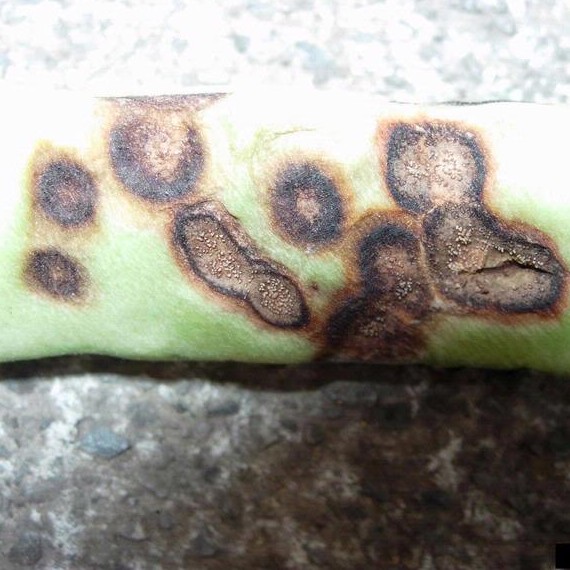
- Leaves, stems and pods of pea are susceptible to infection.
- Small reddish-brown, slightly sunken spots form on the pods .
- These spots are rapidly developing into large, dark-sunken lesions on plants .
- In moist weather, masses of pink spores develop on these lessons.
- Infection of the leaves causes blacking along the veins particularly on the under surface.
Management of Rust disease in Wheat
-
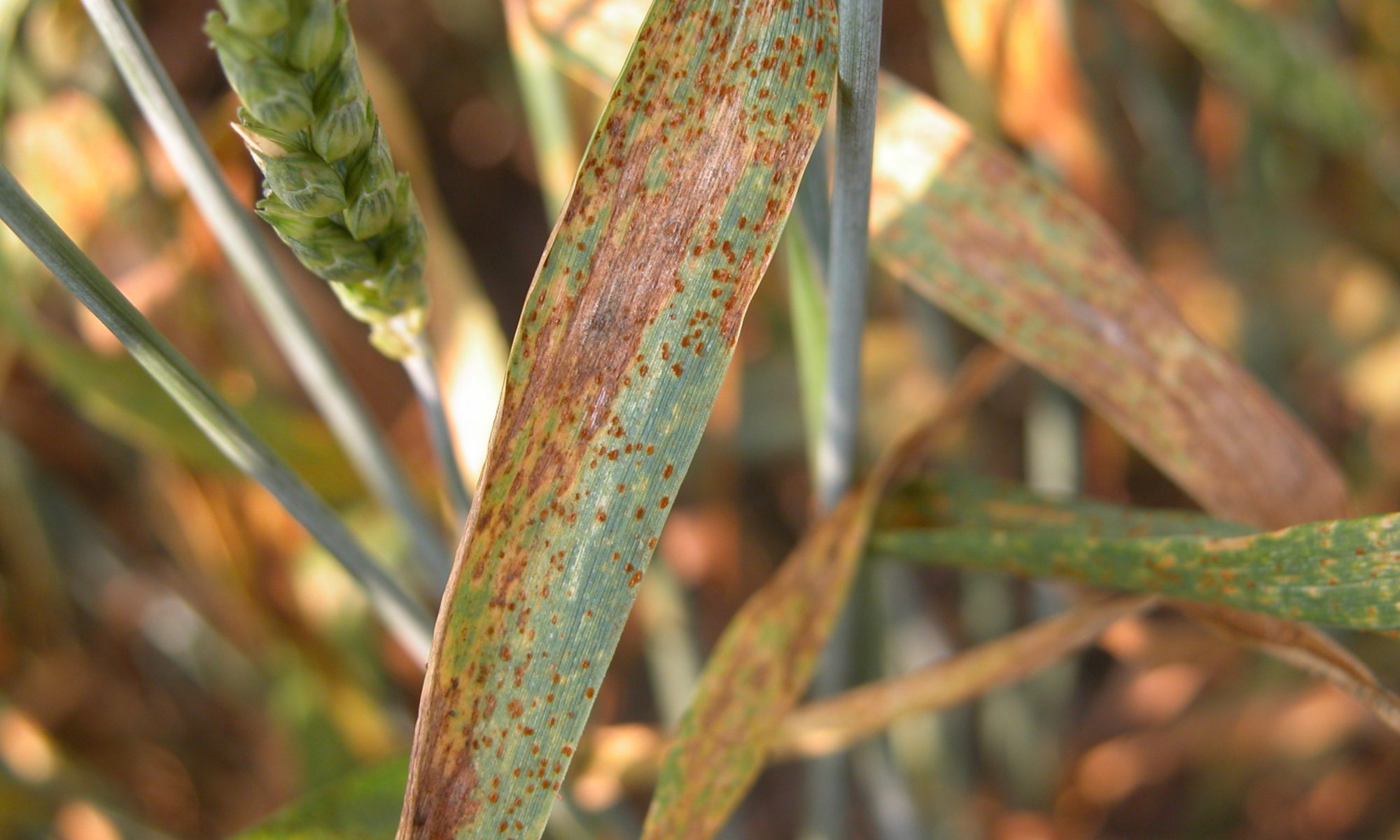
- Leaf rust is caused by the fungus.
- The first signs of the disease (sporulation) occur 10-14 days after infection
- Leaf rust produces reddish-orange coloured spores which occur in small, 1.5 mm, circular to oval-shaped pustules.
- These are found on the top surface of the leaves, distinguishing leaf rust from stem rust which is found on both surfaces of the leaf.
- The spores require 15 to 20ºC temperature and free moisture (dew/rain/irrigation) on the leaves to successfully infect wheat.
Management-
- Crop rotation is very important.
- Growing resistant varieties is an economical and environmentally friendly way of disease reduction.
- During the growing season, active crop monitoring is very important for an early detection of diseases.
- Avoid repeated use of fungicides with the same active ingredient.
- Spray Kasugamycin 5% + Copper Oxychloride 45% WP 320 gm/acre or Propiconazole 25% EC 240 ml/acre.
Like and share with other farmers by clicking on button below
ShareIdentification of wheat rust
- Leaf rust is caused by the fungus.
- The first signs of the disease (sporulation) occur 10-14 days after infection
- Leaf rust produces reddish-orange colored spores that occur in small, 1.5 mm, circular to oval-shaped pustules.
- These are found on the top surface of the leaves, distinguishing leaf rust from stem rust which is found on both surfaces of the leaf.
- The spores require 15 to 20ºC temperature and free moisture (dew/rain/irrigation) on the leaves to successfully infect wheat.