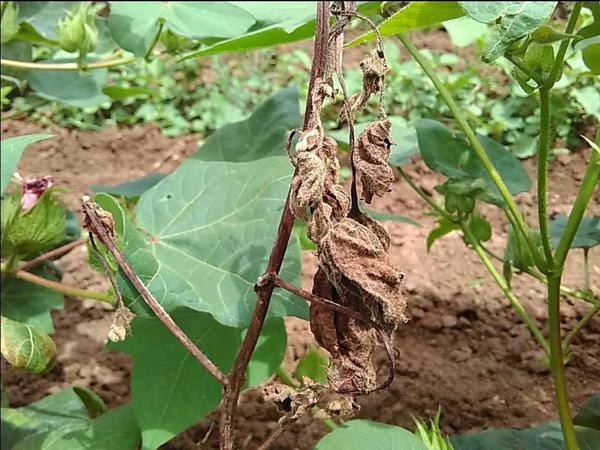
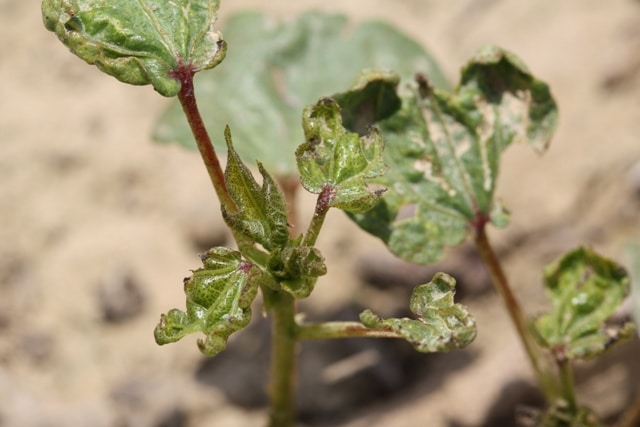
- This disease occurs in both native and American varieties of cotton.
- Usually, it occurs after the first monsoon rains the plant enters a state of 30-40 days.
- Symptoms of root rot disease appear circular or field crops start drying up in circular patches.
- The affected plant roots are Melt When you uproot the plants it’s easily uprooted.
- Trichoderma viride should be used as soil treatment at the rate of 500 gram/acre.
- Carbendazim 12% + Mancozeb 63% WP @ 500 gram / acre or thiophanate methyl 70% WP @ 500 gram / acre or Trichoderma viride @ 250 gram / acre
Monsoon rains are heavy in MP, it will continue to rain for the next 24 hours
It has been raining in many areas of Madhya Pradesh since Friday morning. Farmers of the state are also happy with the timely arrival of monsoon and getting heavy rain. It is raining heavily in the capital Bhopal in the month of June itself. The situation is that on Wednesday, Thursday, and Friday, the rain quota of June has almost doubled from 13.08 cm to 24.68 cm.
According to meteorologists, till now in the month of June, till Friday night, 32.25 cm of rain has been received. This is 27.65 cm more than the normal rainfall so far. According to the weather center, heavy rains are expected in many cities of Bhopal, Hoshangabad, Jabalpur and Rewa divisions on Saturday as well. From June 20 to 22, there will be chances of rain in eastern Madhya Pradesh, Bhopal, and Hoshangabad divisions.
Source: Bhaskar
ShareGramophone’s advice increases cotton farmer profit from 6 lakhs to 12 lakhs
The Government of India is taking many major decisions on the goal of doubling the income of farmers. Gramophone, a true partner of farmers, is doing something similar at its level since 2016. During the last 3 to 4 years, the income of many farmers associated with Gramophones has doubled. One of them is Mukesh Mukati, a cotton farmer of Sali village of Rajpur tehsil under the Barwani district. Mukesh had been cultivating cotton for many years and he used to get a little profit. But he was not completely satisfied with this and in the meantime, he came in contact with Gramophone.
After coming in contact with the gramophone, Mukesh started taking the advice of experts for cotton cultivation and took care of everything that the experts told him during the harvest cycle. As a result, Mukesh’s agricultural costs were reduced considerably and profits doubled.
Earlier Mukesh used to earn up to 6 lakhs from cotton cultivation on his 14 acres of land. But on the advice of Gramophone, when he did farming, his earnings doubled to 12 lakhs. Not only this, the cost of farming which used to go up to 3 lakhs, has now come down to 2 lakh 15 thousand.
If you also want to make a similar difference in your agriculture like Mukesh, then you can also join Gramophone. To connect with Gramophone, give a missed call on the toll-free number 18003157566 or login to the Gramophone Krishi Mitra app.
ShareFertilizer Management at the time of Sowing in Maize Crop
- Among the main food crops in the world, maize is the third main crop after wheat and paddy.
- The main reason is its productivity – because its production capacity is 25-100 percent more than wheat and paddy. and 15-30 June Kharif season is the most suitable time for sowing.
- For maximum benefits, soil testing is necessary before sowing. Before sowing, well-decomposed cow dung manure/fym should be mixed at the rate of 4–6 tonnes per acre broadcast in the field.
- Adequate quantity of fertilizer and fertilizer should be given at the appropriate time to obtain maximum yield by hybrid and conglomerate varieties of maize.
- Urea @ 25 kg / acre, DAP @ 50 kg / acre and MOP @ 40 kg / acre at the time of sowing, broadcasting in the field.
- Along with this, the farmer can also use the Maize Samriddhi Kit. The total quantity of this kit is 2.7 kg/acre. In this kit, you will get everything that is needed for the maize crop. This kit has many products attached.
- The Maize Samriddhi Kit consists of four types of bacteria ‘nitrogen fixation bacteria, PSB, and KMB.zinc bacteria solubilize Insoluble zinc and makes it available to plants. It is one of the most important micronutrients for plant growth.
- Maize Samriddhi Kit kills pathogens that occur in soil and seeds, helps in the growth of flowers, fruits, leaves, etc. as well as helps in the growth of white roots.
Importance of Azospirillum in Paddy Crop
- Azospirillum is an organic microorganism that plays a very important role in paddy crop.
- Paddy crop growth can be increased by the use of azospirillum.
- In Paddy plants, Azospirillum cells spread from the ground to the tissues above the ground.
- Azospirillum protects plants from abiotic stresses and promotes plant growth.
- This azospirillum bacteria produces atmospheric nitrogen to the paddy crop as nitrate.
- At the time of transplanting or before planting of paddy seedlings if we use azospirillum culture Paddy crop can be protected from any kind of damage
Purchase of gram, lentil and mustard at support price in Madhya Pradesh till this date
In Madhya Pradesh, procurement of gram, lentil, and mustard at the minimum support price is currently in progress and the last date of this process has now been extended to 29 July. Previously, the last date for procurement by the Agriculture Department was kept on 15 June which has now been extended.
Along with this, it has also been told that now the purchase will be made only from the farmers called by sending SMS. The purpose of doing this is to make storage arrangements simultaneously. On this issue, the state agriculture minister Kamal Patel has appealed to the farmers to keep their crops at home. Every grain of registered farmers’ produce will be purchased.
It is worth noting that so far six lakh 58 thousand tonnes of gram has been purchased in Madhya Pradesh at the support price and farmers have been paid Rs.3,700 crore as its value. Explain that this purchase process was started from May 29 and it will run for 90 days.
Source: Nai Dunia
ShareHow to manage Wilt disease in soybean
- Wilt disease is a growing soil-borne disease in soybean production areas.
- It can be difficult to differentiate other diseases and wilt.
- This disease is caused by cold temperatures and wet soil during early vegetative growth, plants are infected during the early reproductive stages, but symptoms appear later.
- Due to wilting, there is brown discoloration in the roots and stems, and the leaf becomes chlorotic. To prevent this disease, soil treatment, and seed treatment are very important.
- Fungicide is used for the prevention of this disease.
- Spray Propiconazole 25% EC or Kasugamycin 5% + Copper oxychloride 45% WP @ 300 g / acre or Thiophanate methyl 70% WP 500 g / acre.
- In biological treatment, use Trichoderma viride @ 500 gram / acre or Pseudomonas fluorescens @ 250 gram / acre. These fungicides are used as soil treatment and seed treatment.
- In case of more problems, also use a decomposer before sowing the crop in the field.
Soybean Weed Management
Soybean crop is the main crop of the Kharif season. Due to sowing in kharif, there are a lot of outbreaks of weeds in soybean crop.
For the first use of germination (1-3 days after sowing): –
Imazethapyr 2% + Pendimethalin 30%EC @ 700 ml / acre Or Diclosulam 84% WDG @ 12.4 g / acre
12 -18 days after sowing:-
Fomesafen11.1% + Fluazifop-P-Butyl11.1%SL @ 400 ml / acre fusiflex) Or Chlorimuron Ethyl25% @ 15 gram / acre or Or Sodium acifluorfen16.5% + Clodinafop propargyl 8%EC @ 400 gram/ acre or Or Imazethapyr 10%SL @ 400 ml / acre or Propaquizafop 2.5%+ Imazethapyr 3.75% WP 800 ml/acre
ShareAfter monsoon entry in MP, Meteorological Department warns of heavy rain in 17 districts
In Madhya Pradesh, the monsoon has knocked on its due time and due to this, there is a period of rain and storm in many districts of the state. With the arrival of the monsoon, rains started in 22 districts of the state including the capital Bhopal on Monday.
According to the Meteorological Department, the monsoon has reached most of the districts of Hoshangabad, Indore, Shahdol, and Jabalpur divisions. Apart from this, the monsoon has also made its presence in some districts of Ujjain division. Along with this, warnings of heavy rains have also been issued in 17 districts during the 24 hours coming from the Meteorological Department. These districts include Anuppur, Barwani, Betul, Chhindwara, Dhar, Dindori, Hoshangabad, Harda, Jhabua, Khargone, Narsinghpur, Rewa, Seoni, Shahdol, Sidhi, Singrauli, Umaria.
The monsoon is expected to move towards eastern Madhya Pradesh during the next 48 hours. The northern limit of monsoon is passing through Kandla Ahmadabad, Indore, Narsinghpur, Umaria, and Ballia.
Source: Nai Dunia
ShareThrips Management in Cotton
- In cotton, when the first monsoon rains occur, sucking pests start in cotton .They suck the leaves and buds with their sharp mouthpiece, the leaves may turn brown on the edges, Or leaf may curl. at and plant may dia.
- In these pests like thrips, aphid, jacid affected plants are very high.
- The use of low cost chemicals is beneficial for the management of these pests.
- Profenophos 50% EC @ 400 ml / acre or Abamectin 1.9% EC @ 150 ml / acre or spinosad 45% SC @ 75 ml / acre
- Lambda Cyhalothrin 4.9% CS @ 200 ml / acre or fipronil 5% SC @ 400 ml / acre
- Acetate 50% + Imidacloprid 1.8% SP @ 400 g / acre or Acetamiprid 20% SP @ 100 g / acre
- Metarhizium anisopliae @ kg / acre or Beauveria bassiana at the rate of 250 gm